NFT (non-fungible tokens) burst in popularity in 2021 as many investors detected its potential.
Subsequently, however, the attitude towards the NFT space resembled a sine wave. Some people predicted success no less than that of Bitcoin.
Some saw it as another tulip mania and predicted the imminent end, with the insufficient daily value of traded NFTs, the collapse of Terra (LUNA), and the low number of users that bought or sold NFTs.
Nevertheless, NFTs are still around today, largely due to their successful use in certain areas, such as gaming.
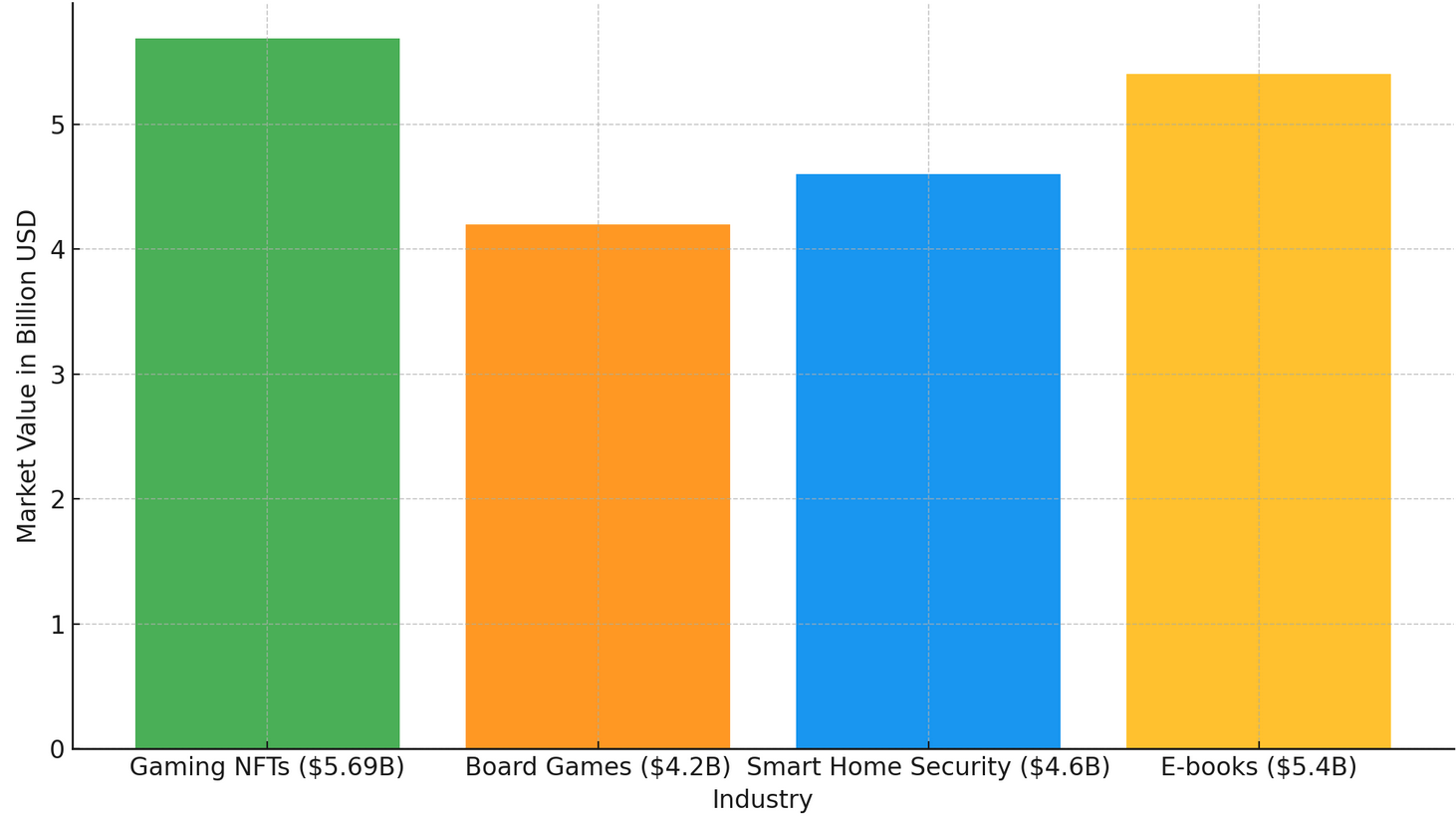
Now, the NFT gaming market is valued at $5.69 billion, which means it surpasses some well-known industries, such as board games ($4.2 billion), smart home security ($4.6 billion), and even e-books ($5.4 billion).
Market Value Comparison: Gaming NFTs vs. Other Industries
What Are NFTs in Gaming and How Do They Work?
Basically, an NFT is a digital certificate that acknowledges a certain person as the proprietor of a virtual asset with no equivalent to it. These certificates are created and sold on blockchain and are regulated by smart contracts.
NFT technology always refers to something exclusive: no matter how many digital duplicates there are, there is only one authentic asset. This way, an NFT owner practically buys ownership rights.
NFT games, in turn, are video games that use non-fungibles as a central part of their gameplay. NFTs here usually represent different in-game artifacts, such as game characters, skins, weapons, and virtual land.
The process of playing NFTs is hardly different from traditional games, except for the possibility of getting some profit out of it and reliance on blockchain networks, such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Polygon.
It usually involves playing the game to earn rewards, storing them in a crypto wallet, and using or selling them (at will) inside or outside the game’s ecosystem.
Also, NFT games are not tied to any specific genre. They can belong to RPGs, strategy games, card games, MMOs, arcades, etc.
Blockchain Standards for NFT Games
To ensure interoperability and functionality, token games typically use special NFT standards. There are quite a few standards in the blockchain industry, but presently, the most commonly used ones include ERC-721 and ERC-1155:

- ERC-721 – ERC-721 represents unique, indivisible assets like rare game items or collectibles. It serves as proof of ownership for limited-edition digital or real-world assets.
- ERC-1155 – ERC-1155 is the extension of ERC-721, which was developed by the Enjin Project game development team, a blockchain game solution company, to overcome the shortcomings of ERC-721. The emergence of ERC-1155 allows users to share multiples of ERC-721 by a single smart contract. For example, if users want to sell hundreds of gaming items in a game, they can use ERC-1155 to transfer them all in one go.
The Benefits of Making NFT Games
If from the players’ point of view, the benefit of switching to NFT games is clear (they have a direct opportunity to earn money by selling this or that artifact), then what benefit do the creators of NFT development services have?
Monetization
All NFTs are connected to a larger network consisting of many other parts built on top of a blockchain. Players who win or acquire in-game assets can immediately visit NFT marketplaces and freely buy, sell, or swap their purchases.
For game developers, this open economy also uncloses new paths to monetization. For example, developers can earn revenue by selling initial NFTs, earn royalties each time the NFTs are re-sold on a marketplace, and even charge transaction fees on in-game purchases or trades.
NFTs also generally have a monetary premium over their traditional in-game item look-alikes. They are more costly to produce, which leads to a greater price.
Sovereign Ownership
Traditionally, the gaming supply chain consists of the following participants: Developers (e.g., Respawn Entertainment), Publishers (e.g., EA), Distribution Platforms (e.g., Steam), and Players.
Publishers typically take the biggest cut of game sales (around 70%) and inner purchases as they direct funding, marketing, and distribution.
Digital distribution platforms take around 30% of each sale. Game developers usually get paid upfront by the publisher or receive a revenue share (often a smaller percentage).
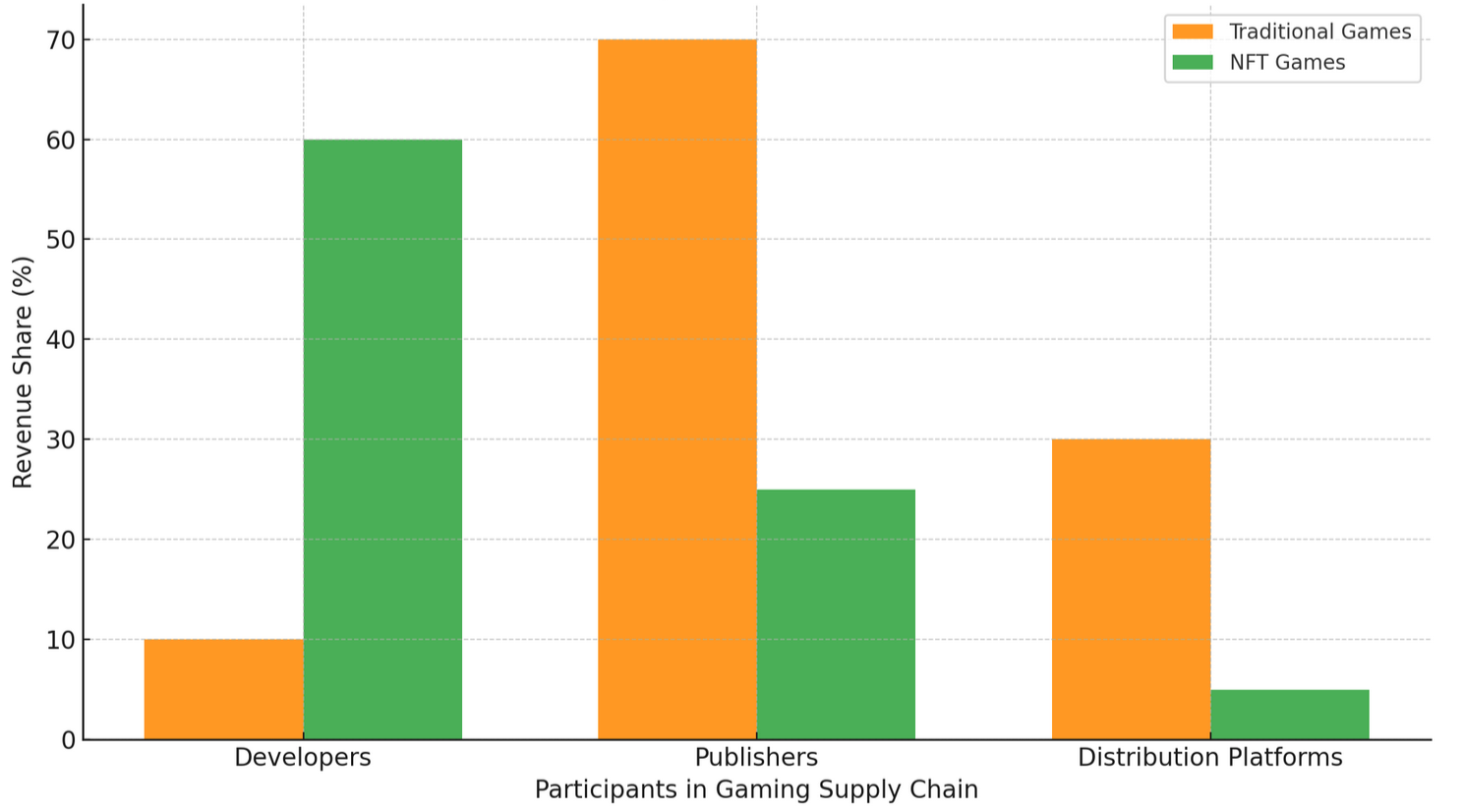
Revenue Share Comparison: Traditional vs. NFT Games
In NFT games, the basic relationships between developers, publishers, and digital distribution platforms are similar, but there are some fundamental distinctions due to the nature of blockchain.
Game developers create the game and the virtual items (coins, cards, and other memorabilia). They may earn money through the initial sale of objects or subsequent resales.
Game publishers (if separate from the developer), similar to traditional games, can also have a share in the game’s revenue, but often their percentage is smaller than the developer’s because they typically don’t hold ownership of the NFTs themselves.
Digital distribution platforms may control the sale of NFT assets, but they typically take a small commission (usually around 2.5-5%) from each NFT sale or transaction.
So, for NFT-based games, developers typically earn the most, especially if they retain ownership of the NFTs, as they can earn from initial sales and further resale royalties.
Interoperability
NFT games made on the same blockchain are connected through a shared infrastructure, which makes it possible for tokens to move freely between different applications.
For example, an NFT that you earn within the game can be used in another game (or games) or even repurposed for a different use within that new game.
Many Web3 projects create NFTs hoping to spark a lot of new development that takes full advantage of this interoperability.
They release tokens with the hope that other users will buy them, play them, and even take out loans from DeFi protocols against their NFT, all on a single, comprehensive platform.
How to Create an NFT Game: All Ins & Outs
For many, creating an NFT game is very similar to making traditional games. In reality, gaming token manufacturers must take their time to nail every single aspect of the product.
Otherwise, the game can quickly fall out of popularity and both inner tokens and currency become worthless.

A step-by-step guide to creating an NFT game
Step 1: Point Out the Chief Quality of Your Game Concept
Before beginning the development process, you must shape a clear concept of what kind of NFT game mechanics you want to produce.
The first decision is to choose the game genre because it will move the entire gameplay mechanics.
The most popular options we’ve already listed above. It can be RPGs, where players own and upgrade NFT characters and weapons, metaverse games, where players can buy, sell, and develop virtual land, trading card games, strategy games, and quests.
Next, you need to decide on the game’s reward system. Per a play-to-earn (P2E) model, players gain NFTs and cryptocurrency through playing. A traditional model simply supports the use of tokes but they aren’t the main way to earn. Many games, by the way, employ a hybrid approach, blending both directions.
The next question is how NFTs will be used in your game. Will they represent characters, weapons, skins, land, or internal money? Can players trade, swap, or lease them? Will there be deluxe objects that are harder to get? Nailing these particulars will make a proportional game economy.
Also, you must think about how players will interact with the game. Some common ways include battling, trading, exploring, or crafting new items.
Will there be a game token used to buy and sell NFTs? How will players progress—by leveling up, completing quests, or winning rewards?
Finally, consider your potential adherents. Is your game for occasional enthusiasts or hardcore gamers? Do they belong to crypto-savvy users or stick to a more traditional side? Will the game be available on PC, mobile, or as a browser-based game?
Step 2: UX/UI Game Design
A great user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) make an NFT game fun and easy to play. Players should be able to scour the game, classify their NFTs, and complete transactions without confusion, even if they’re new to blockchains.
All inner menus must be easy to steer, and players should quickly find what they seek, be it their inventory, the marketplace, game settings, or crypto wallets.
New players should also get a brief tutorial on how NFTs work in the game, so they don’t feel lost. Buying, selling, and upgrading assets should be fast and trouble-free, with clear feedback to submit actions.
Visual design is not any less important. Game assets such as characters, cards, or land must be visually compelling and of high quality.
Adding animations and effects always adds a touch of excitement to NFT interactions, while an overall art style maintains an interesting game world.
Step 3: Choose a Development Provider to Delegate Your Project
Building an NFT game requires expertise in blockchain, smart contracts, game design, and backend systems. Instead of governing every single piece yourself, you can hire a professional blockchain game development company to take care of the technical side.

An NFT game development company will help you choose the best blockchain for your game (e.g., Ethereum blockchain, Binance Smart Chain, Solana), pick the correct smart contract language, such as Solidity or Rust, and naturally weave non-fungible tokens right in the game.
Your team will also plan out the game’s economy and NFT marketplace. They’ll structure the in-game currency, rewards, and token trading system to make the game amusing yet profitable.
Another point is smart contracts. Blockchain developers will build thorough smart contracts to control NFT ownership, in-game transactions, and gameplay mechanics.
On the backend, the team will set up game servers, manage databases, and connect MetaMask or Phantom wallets so players can use their crypto belongings.
Step 4: Testing and Protection Assessments
Prior to the final release of your NFT game, it’s necessary to carry out some reviews to find and settle problems before they affect the game. Beneath is a rough checklist of the main assessments that must be done:
- Smart contract audits certify the enforced terms of agreements are free from errors, fraud, and unintended outcomes.
- Performance testing prevents defects or crashes on different devices.
- NFT transaction inspections prove buying and selling NFTs works correctly.
- Game economy balancing confirms rewards are fair and the game’s economy can withstand stress without structural distortion.
- Anti-cheat systems stop players from unlawfully taking advantage of the game.
- Safeness testing deters hackers from thieving NFTs or messing with the game.
- Beta testing with real players can collect suggestions and resolve any remaining problems.
By and large, all these checks can be done in two ways: manual or automated. Manual testing involves real people playing the game and looking for problems.
Automated testing uses special tools to quickly review the game and smart contracts for gaps, without the need for a person to do it manually.
Common tools for testing include:
- Truffle and Hardhat for scanning the smart contracts.
- Selenium for independently testing the game’s interface.
- MythX and Certik for inspecting the safety of smart contracts.
Step 5: Presenting Your NFT Game
After all the hard work of development and testing, you can submit the game. The first thing developers will do is deploy the game on a testnet to simulate actual trades and interactions without using real money or purchases and only after on the mainnet, where players can apply real tokens and inner currency.
Popular NFT Game Examples to Refer to When Making a Game
Today, NFT games exist in various forms. Some produce entirely new lands developed by enthusiasts. Others take inspiration from classic games enriched by the extra benefits of non-fungible objects.

These examples showcase the range of opportunities for designing fascinating and creative NFT-based adventures.
Gods Unchained
Gods Unchained is an NFT trading card game (TCG) similar to online card game fans like Hearthstone and Legends of Runeterra. The players participate in competitive, player-versus-player (PvP) fights with a deck of cards, trying to outsmart their opponents and win.
In this game, players can buy randomized NFT card packs using the game’s native currency, which can be earned through gameplay or purchased directly from the marketplace.
After players receive the cards, they fully own them as NFTs, and can freely sell or barter them on the in-game marketplace.
Dookey Dash
Dookey Dash, a limited-time NFT game created by Yuga Labs (inventors of the Bored Ape Yacht Club, or BAYC), presents a new approach to non-fungible tokens in gaming.
Access to the game is made possible via NFTs—awarded to BAYC owners or traded as short-lived access passes on the open market.
The game itself is an endless runner, similar to Subway Surfer, where players compete on a leaderboard for the highest score. Those at the top of the leaderboard earn NFT rewards with future utility within the BAYC universe. Players can also purchase powerups to enhance their gameplay.
Dookey Dash is just one of the NFT games that are integrated into a larger metaverse and use NFTs both as a gatekeeper and a reward system. Although this arrangement may be harder for small games to accomplish, it shows that NFTs can scale gaming, enforce social status, and fuel the demand for virtual rewards.
Loot
Loot is not your typical NFT game. It started out as a series of text-based NFTs without images, each of which contained a list of items like “Wool Sash” or “Leather Boots of Enlightenment.”
Loot was devised as a platform for collaborative world-building. Developers and players alike could take these items and, essentially, use them as Legos for their own projects, be that a loot-based raid game or even a puzzle quest.
Loot is an example of how NFTs can kindle creativity and community-driven growth. Instead of a specific game, Loot was built upon by its community and each NFT became a component of the world. It provided the gateway for infinite possibilities within gaming and digital storytelling, energized by community passion.
Case Study: How We Built an NFT Game for Our Clients
At SCAND, we’ve worked on multiple blockchain-based gaming projects, helping clients integrate NFTs, smart contracts, and decentralized marketplaces into their games.

One of the most interesting cases was creating smart contracts for an NFT gaming platform in the metaverse. We realized token staking, ERC-20 token management, blockchain lottery, and NFT buying/minting.
Our solution also included blockchain integration with Ethereum and Binance Smart Chains to offer a holistic dip to the users and simplify in-game acquisitions, governance, and social quest gameplay.
FAQ
What is the cost to create NFT games?
The cost of the game development process can greatly differ depending on complexity, choice of blockchain, and number of development staff. Less complicated NFT games can run between $50,000 to $100,000; more complex and large-scale projects can go upwards. Overall, NFT game development costs may reach up to $500,000.
What is the best blockchain for NFT game development?
Ethereum is the most widely used option, but there are other alternatives, such as Solana, Flow, and Polygon with advantages such as cheaper fees and quicker transactions. The appropriate blockchain will be determined by the scalability requirements of your game, development tools, and desired user experience.
Can I develop an NFT game without knowing how to code?
Even though there are plenty of no-code platforms, NFT game development on a blockchain needs profound blockchain knowledge. It is better to work with proficient developers or outsource to a game development company for a good quality game.
How do NFT game projects make money? Is it worth investing in NFT game development services?
NFT games make money via a variety of means, including trading fees, internal assets, resale royalties, and ads.
How do I become safe in an NFT game?
To avoid hacks and fraud, you must carry out frequent safety audits, bug bounty programs, secure smart contracts, and anti-cheat. All these factors are necessary to protect the game itself and its players.
What are the key elements of the game that runs on NFTs?
An NFT-based game features unique NFT items, a well-balanced in-game economy, blockchain integration, smart contracts, and an engaging game loop. These ensure that your game is both functional and appealing to players.
How do NFT standards impact game development?
NFT standards like ERC-721 and ERC-1155 define how NFTs in the game function. Choosing the right standard is crucial for smooth NFT integration and a seamless gaming experience.
Do I need a license to develop NFT games?
While you don’t need a specific license to make an NFT game, certain aspects like game engines, intellectual property, and blockchain technologies may require legal considerations. Consulting experts can help navigate compliance.
What game engines can be used to develop a crypto NFT game?
If you want to create your own NFT game, you’d better opt for some popular game engines, such as Unity and Unreal Engine. These engines allow developers to create unique game worlds and integrate blockchain functionality through plugins and SDKs.
How can game developers generate revenue from NFT games?
Developers can earn from NFT sales, transaction fees, royalties, in-game purchases, and play-to-earn NFT mechanics. Creating a sustainable economy within the NFT ecosystem is key to profitability.
What are some examples of NFT games?
Popular NFT games include Axie Infinity, Gods Unchained, and The Sandbox. These games showcase different types of NFT integration, from collectible card games to metaverse adventures.
What is required for NFT creation in a game?
To integrate NFTs into the game, developers need smart contracts, a blockchain network, an NFT marketplace, and game assets that can be tokenized. Choosing the right blockchain technologies is crucial.
How do you test your NFT game before launch?
Testing involves smart contract audits, gameplay balance checks, security assessments, and beta testing with NFT communities. This phase of NFT game development ensures a stable and engaging game experience.
How do mobile NFT gaming apps differ from traditional games?
Mobile NFT apps incorporate blockchain-based assets and often use crypto wallets for transactions. Unlike traditional games, they allow players to trade and own in-game assets permanently.
What is the next step after developing an NFT game?
After building an NFT game, the next step is to create a marketing plan, engage NFT communities, and launch your NFT game on the appropriate blockchain. Sufficient post-launch support is crucial for long-term success.