Have you ever encountered Dave, EarnIn, Brigit, or Chime apps? All these are loan software solutions. But isn’t it banks that issue loans?
Frankly speaking, banks like JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, and Wells Fargo still have the largest consumer loan volumes. Nonetheless, neobanks, digital banks, and other alternative providers are gradually increasing their market share.
For example, the value of the Brazilian neobank Nubank has moved from $58 million in 2019 to around $3.2 billion in 2023. The market share of buy now, pay later platforms, such as Klarna and Afterpay, has also risen all over the world.
Moreover, in 2024, digital banks issued loans amounting to about $13 trillion, which, although 15 times less than the amount provided by traditional banks ($200 trillion), is also quite a lot in absolute terms.
Taking all this into account, it becomes clear that developing and having a loan application can be a worthwhile endeavor. But how to build such a platform to make the most out of software development services?
What Is a Loan Mobile Application and How Does It Work?
A loan app is a mobile software solution that makes the lending and borrowing process possible by enabling users to apply for loans, get money, and watch their financial obligations.
In simpler terms, these apps bring borrowers and lenders together, who can be individuals or financial institutions, and use sophisticated technologies to initiate and ease the application process.
Credit apps typically feature simple, user-friendly screens and dashboards that allow borrowers to apply for loans, upload documents, and receive approvals or rejections online.
When approved, funds are deposited into the account of the borrower, and repayment conditions are set. In most cases, credit apps also provide lenders with loan tracking, risk governance, and portfolio administration.
Market Overview of Loan Lending Mobile App Development
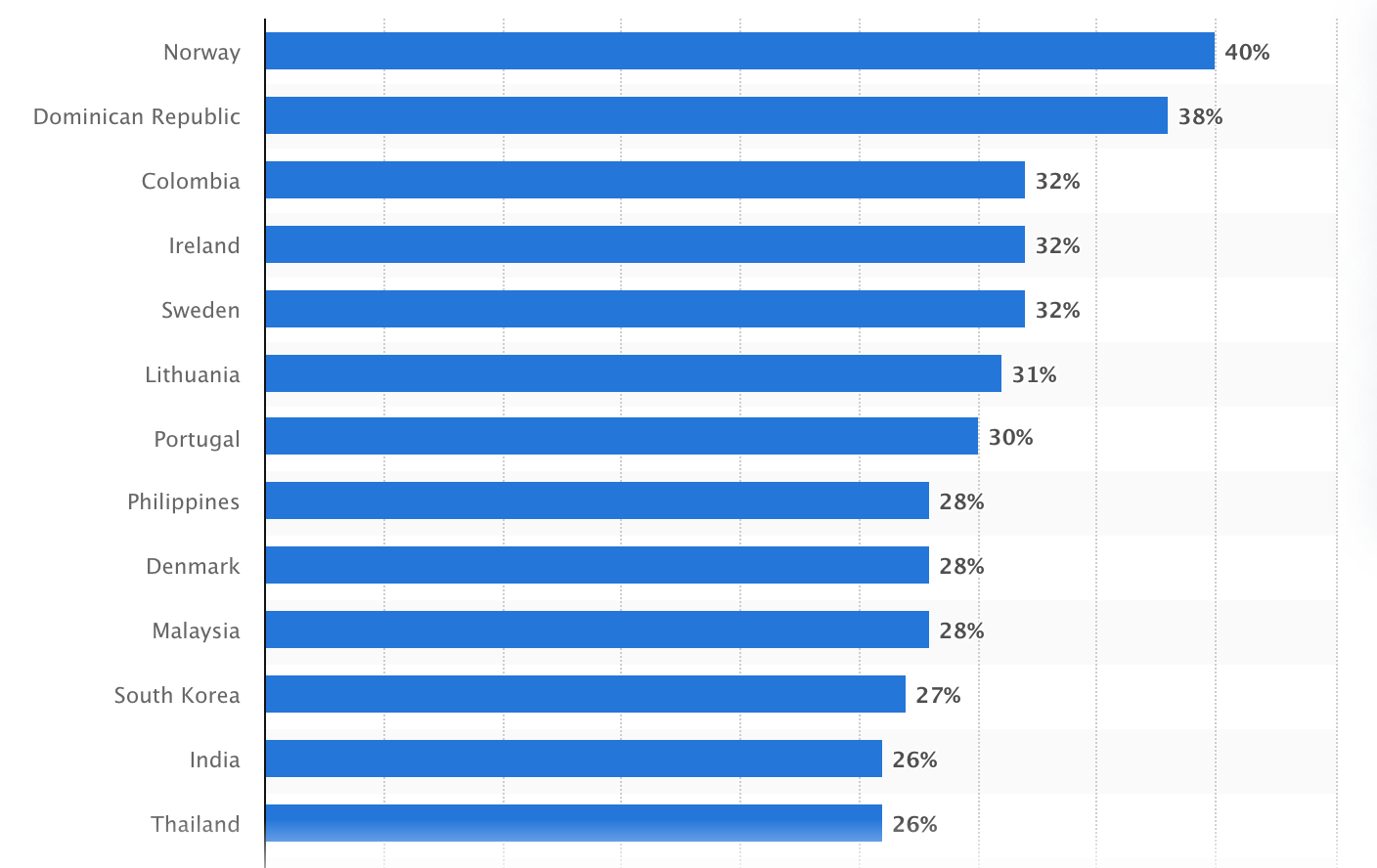
It is an undeniable fact that society has become more consuming. When looking at the credit owners in countries around the world, it becomes clear that more and more people rely on loans to cover their financial needs.
In Colombia, this number reaches 32%, and in the Dominican Republic 38%. But Norway remains the leader, where the number of credit borrowers is 40%. But why do people look for alternative ways to get loans?
Share of loan owners worldwide, as of January 2025, Statista
Traditional banking systems often involve lengthy paperwork, physical transactions, and extensive approval procedures that are no longer comparable with the modern pace of life.
Mobile lending applications, in turn, provide a much better equivalent, where a lender can take credit instantly, in some cases even within minutes.
Plus, they are often equipped with machine learning algorithms that quantify creditworthiness using alternative data, such as mobile phone usage, spending patterns, and social media posts. This way, a lengthy credit history check is normally not needed.
In addition, according to Market Research Future, there are a number of other factors that contribute to the growth of credit applications. These include:
- Rising smartphone penetration
- Affordable mobile app development
- Regulatory support for fintech developments
- The advancement of peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms.
- The emergence of microcredit offerings
- The adoption of AI, blockchain, and automation

Types of Loan Solutions: Peer-to-Peer, Microloan, and Traditional Apps
Not all credit apps are alike. Some connect borrowers with individual lenders, some offer tiny, short-term loans, and some operate just like old-school banks—but all on your phone.
Let’s break down the three main types of credit applications: peer-to-peer (P2P) lending applications, microloan tools, and traditional lending platforms—so you know what differentiates each.
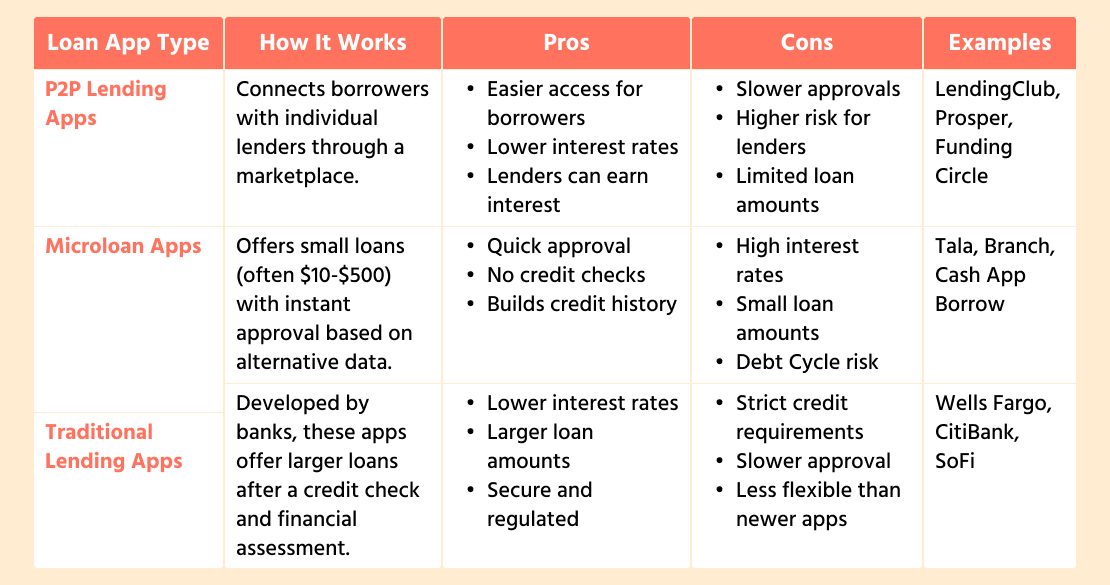
Types of Money Landing App Solutions, Comparative Table
P2P Lending Apps: Borrow Directly from People, Not Banks
Peer-to-peer lending tools operate like a marketplace through which one individual borrows money from another individual as opposed to a bank or other financial institution.
The app acts as the middleman that connects lenders with borrowers, determines the terms of agreements, and provides secure transactions.
How it works:
- Borrowers complete a form, apply for credit, and get matched with lenders ready to subsidize their requests.
- Lenders choose which loans they want to fund, either manually or through automated systems that match them with borrowers based on risk level.
- Interest rates, in turn, are generally set by the platform according to the borrower’s risk score.
Popular examples: LendingClub, Prosper, Funding Circle
Pros:
- Easier access to loans, even for those with limited credit history.
- Lower interest rates compared to traditional loans.
- A great way for private lenders to earn money in terms of interest.
Cons:
- Not always immediate—approval of the credit could take a few days.
- Greater risk to lenders in case the borrowers default.
- Credit amounts may be smaller than in banks.
Microloan Apps: Small, Short-Term Loans for Basic Supplies
Microloan apps are designed to provide small loans, typically for those who do not qualify for standard credit, such as people in emerging economies where penetration of financial products is low.

Microloan solutions are different from P2P platforms as they are usually secured by a firm or fintech company rather than individual lenders.
How it works:
- Users apply for small amounts (often between $10 and $500), typically for short-term use.
- The app employs AI to scan data and decide if a borrower is eligible.
- When approved, the credit is instantly disbursed, and repayments are scheduled automatically.
Popular examples: Tala, Branch, Cash App Borrow
Pros:
- Very fast approvals—some credits are approved within minutes.
- No traditional credit checks are required.
- Helps people build a credit history.
Cons:
- High interest rates since these are short-term, high-risk loans.
- Borrowers can fall into a debt trap if they don’t plan repayment properly.
- Credit amounts are restricted, and they’re not particularly suitable for large expenses.
Traditional Apps: Banks and Financial Institutions Go Digital
Banks, credit unions, or financial institutions develop traditional platforms to digitalize their loan offerings. These apps work the same way as visiting a bank to apply for a loan—only online.
They’re best for people who are looking for larger, more structured loans, such as personal credits, car loans, or home mortgages.
How it works:
- Borrowers apply for a loan via the app.
- The bank reviews their financial status, income, and credit history.
- After approval, the funds are disbursed and payment arrangements are made in regular (usually monthly) installments.
Popular examples: Wells Fargo Personal Loans, CitiBank Loan Solution, SoFi
Pros:
- Larger loan amounts are available.
- Safe and regulated by financial authorities.
Cons:
- Stringent requirements—borrowers must provide a positive credit history and evidence of income.
- It will take longer to qualify than microloan or P2P applications.
- Less freedom compared to fintech loan solutions.
Which Loan Solution Is Right for Lending Business?
If you’re an entrepreneur creating a financial app, what type you create depends on whom you want to serve.

If you want to offer quick, short-term credits to people with fewer credit histories, create a microloan app. If you want borrowers to borrow from people instead of banks, a type is more appropriate.
However, if you are looking for more substantial financing, like business or personal loans, a classic app is definitely the best option.
Key Benefits of Money Lending App Development
There are many benefits to creating your own credit application. For example, having such an app means that you can make money in a number of ways, apart from loan interest. You can take and offer:
- Loan fees
- Premium plans
- Late payment fees
- Partner deals
- Ads inside the app
The second benefit of having your own app is that you can cut out the middleman. This means you don’t have to share your profits with banks or other financial institutions.
No matter if you opt to offer peer-to-peer lending, microloans, or standard financing, making your own app means you can set your terms, rates of interest, and charges.
The next advantage is that you can reach more people given the fact that alternative providers are usually open to a wider audience and can serve those who have been rejected by traditional institutions.
Unlike banks, who rely on credit ratings to decide whether to lend to a person or not, you can use other sources of information to figure out if someone is worth lending to.
This gives you the chance to help people who may not have a recorded credit history but do need access to money.
Lastly, when you develop your own application, you are completely free to shape it in the way that is most practical for your business. Whether you deal in personal credits, business loans, or services like Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL), you can frame an app that will be suitable for your plans and ideals.
Prerequisites to Start Money Lending App Business
If you’re planning to create a money lending solution, there are a few important actions you need to do before you dive into development. It’s not all tech—it’s also about getting your business in order.

Prerequisites to Consider Before Starting Money Lending App Business
Fill Out a Business Licensing Form
First of all, you need to register your company. This will take some paperwork with your state or local government so that they can officially record you as a lending service.
Set Up Your Company
Next, you’ll have to decide what type of business structure is right for you. Are you going to do it alone, or do you need to have a team backing you up? Most businesses prefer a sole proprietorship, an LLC, or a corporation, each, however, with its own advantages and constraints.
Secure Initial Capital
Now, you will need to source some initial capital to start off. Developing an app, sourcing the legal elements, and running your business costs money.
The amount will depend on how large your app is and what you want to incorporate. You can fund it from personal savings, borrow from someone, get a loan, or even get investors to fund your concept.
If you’re lending money, you’ll also want to make sure you have enough funds to lend to your customers in the first place.
Steps to Create a Money Lending App
Of course, developing applications from scratch is not easy from a technical point of view. At the same time, if you break the whole process down into smaller parts, at least it will become clear in which direction to move:

1. Preliminary Study and Planning
Before you go ahead and create the app, it’s important to do some planning and research. You must know who your app targets, what other apps offer, and how to follow legal requirements in your area to stay compliant.
In this step, it’s also a good idea to create a business plan. It will help you map out how the app will make money, how you’ll market it, and what resources you’ll need.
2. List Primary Features
Next, you will need to establish the most important parts of your application. The most essential are:
- Loan application forms
- A way to check users’ creditworthiness
- A system for approving loans, automated or/and manual
- A system for payment processing
- Security features
- A way for users to track their repayments
By clarifying these features early on, you’ll know exactly what needs to be built and how the app will work.
3. Design the User Interface (UI)
Your app’s UX/UI design literally dictates the way people will interact with it. If your app is disorienting or difficult to use, people aren’t going to stick around.
Start with a straightforward sign-up process and make it possible for users to apply for loans without frustration. When signed in, users should be able to see a dashboard where they can see loan status, upcoming payments, and repayment history.
Make sure the app is suitable for phones as well as tablets. The design needs to be crisp, minimal, and user-oriented. As far as colors go, consider blue or green, which are usually prevalent in finance apps because they confer stability and trust.
3. Choose the Right Technology
The tech stack has a significant role in how the app works and acts. If you are not a technical specialist and do not plan to code yourself, then at least you should decide on the following points.
You’ll need to choose which OS to strive for—should your app be iOS, Android, or both? With cross-platform frameworks such as React Native or Flutter, you can cut yourself some time and deploy for both.
On the backend, you’ll need a reliable cloud service like AWS or Google Cloud. This is where all your data will be stored and processed. You’ll also need to pick a payment gateway, such as Stripe or PayPal to direct transactions.
For security purposes, it is important to encrypt the user data and use fraud-prevention software. The security of the user data should always be given the highest priority.
5. Develop the App
Now, it’s time to start building the app. The most optimal way here is to hire a development team that will take on the frontend (what users see) and the backend (what is run in the background) development.
They will implement all the features you outlined above, thoroughly test them for bugs, and fix problems in advance to avoid larger problems down the line.
6. Add Security Measures
Because your app is going to deal with sensitive financial information, make sure to encrypt users’ data so nobody else can access it.
Implement two-factor authentication (2FA) as well, which offers an extra security layer when people log in, and use fraud detection software to detect suspicious behavior before it turns into a problem.
You also need to be compliant with industry standards and regulations, including GDPR (data protection) and PCI DSS (payment card industry data security standard).
7. Test the App
Before your app sees the world, it’s important to confirm everything works as demanded.
You must check that all features are functioning properly, from loan applications to repayment tracking, test the app for performance, and examine security resilience to catch any vulnerabilities.
By fully testing the app, you’ll prove users have good reception and that the app is safe to use.
8. Announce the App
When the software is ready, get ready to present it to the market. Here, you’ll need to elaborate a marketing program to make it known.
Double-check that your app’s page is visible to everyone in the Google Play Store or App Store and is optimized with the right keywords so people can spot it.
9. Watch and Update
Next, observe the software’s behavior. Note how the users respond to it and see what they suggest. If they identify any flaws or suggest new features, address those problems.
Update your app in order to dispel any doubt, refine existing features, and add new ones. Keep yourself aware of any change in legislation and do your utmost to keep your app legislation-compliant.
Challenges in Loan App Development and How to Overcome Them
How hard is it to create an app if you never dealt with it before? Frankly speaking, like anything worthwhile, it comes with its own hardships. One of the greatest setbacks is matching all economic directives.

If your software product doesn’t adhere to monetary criteria, you may suffer from legal consequences. To demonstrate your progress in this direction, you’d better consult with a licensed attorney knowing all the nuances of financial services.
Speaking of trust, another major concern is data safety. Since loan solutions deal with confidential user records, they become enticing prey for cybercriminals and scammers.
A breach of data or any illegal activity can severely harm the reputation of your app and even lead to massive fines. The safer your app is perceived to be, the more willing your users will feel to share their information.
Next, people usually are very suspicious of money apps. If your app looks below the standards expected or shady, they may steer clear of it.
Another thing you’ll need to pay close attention to is the user experience (UX). The success of any app depends largely on how clear and enjoyable it is to use. If users find it bewildering, perplexing, illogical, or slow, they’ll quickly substitute you.
To make sure this doesn’t happen, design your app to be simple yet high-quality. The lending process should be clearly understood and not subject to misinterpretation.
The next difficulty you’ll come across is credit scoring and assessing risk. Traditional lending systems rely on credit scores to rate borrowers, but what if they don’t have a credit history?
To solve this, use alternative credit scoring models that examine users based on social media activity, payment history, or even behavioral traits like the frequency of on-time bill payments.
AI-based credit scoring software can also help rate borrowers’ creditworthiness, thereby exposing more users to your platform.
Lastly, you may find it hard to retain users. It’s not enough to get users to download your app; you also must keep them involved and coming back.
Offer them tracking of the loan, reminders for repayments, and personalized offers as a sort of incentive. Regular push notifications and loyalty rewards can also maintain users for your application.
Yet above all, keep listening to your users. Their feedback can help you polish the app and keep it applicable.
How Much Does It Cost to Build a Loan App?
When making a loan app, entrepreneurs often ask how much all this is going to cost. The price always depends on many criteria, including how complex the components are, whether the app goes for one or several OS, and whether it’s all made in-house or outsourced to a software development company.
Knowing the approximate expenses can assist you in better allocating your budget. Let’s roughly dissect it:
- Data Collection and Strategy Development: $5,000–$10,000
- Design and Prototyping: $10,000–$15,000
- Development (Frontend and Backend): $50,000–$150,000+
- Quality Assurance: $5,000–$10,000
- Release, Marketing, Sales: $10,000–$20,000
In the initial design and planning phase, you can expect to pay for market investigation, wireframing, and pilot testing. This will normally take you from $5,000 to $15,000, depending on the level of detail you want in your research and how much work the designers will have to do.
If you’re creating it for both iPhones and Androids, you’ll be on the higher end of that range because it will imply having to assemble duplicate versions for each platform.
The development part, where coding and backend work is done, is no less expensive. An MVP providing only the essentials and nothing fancy would be in the spectrum of $30,000 to $50,000.
But if you have ambitions for high-end features, the cost can soar much higher—$70,000 to $150,000 or more.
It is also worth mentioning the price of integrating payment gateways and compliance with bank regulations, which can be in the range of $10,000 to $20,000.
Besides, you’ll need to factor in lasting charges for testing, deployment, and upkeep. Testing commonly amounts to $5,000-$15,000 again depending on the complexity.
Deployment charges less than the other phases, something between $1,000 to $5,000. Annual routine updates, gaps and flaws, and security patches may take you $5,000 to $15,000.
However, the maintenance fee can double if you add new features or come upon any problem requiring emergency care.
The Role of Legal Compliance and Encryption
The major things you have to bear in mind throughout the entire development process are legal compliance and encryption. Why?

Using end-to-end encryption (where data is rearranged and only the intended recipient can unlock it) is essential when dealing with payments and sensitive info. Without strong encoding, your users’ details could be at risk, and that could lead to major irrevocable security breaches or damage to the public image.
Legal compliance, by and large, demonstrates you follow the directions and regulations for lending and supervising financial details in the places where your app runs.
Different regions have different laws about consumer protection, data privacy, and anti-money laundering.
For example, in the US, you must obey the Fair Lending Act, and in Europe, the GDPR has strict regulations about how you govern confidential records.
Neglecting these decrees can land you in some serious trouble, including fines, prohibitions, or even license revocation.
The ICO, for example, has fined British Airways £20m for a consequential data breach that happened in 2018, resulting in the licking of personal data of over 400,000 people, including payment information, names, and addresses.
Well-Known Examples of Money Lending Apps to Refer to When Making Your Own App
When you’re developing a lending app, it can be really helpful to have a sort of role model you can refer to. These lending companies have already tried the waters, so it won’t be such a bad idea to inspire or learn from them to avoid the same errors:
LendingClub
LendingClub is a leading peer-to-peer lending label. It allows borrowers to connect with individual investors who fund their loans. The app offers personal loans, business loans, and even auto refinance.
LendingClub’s clean and simple design along with its solid financial features makes it an ideal template for a peer-to-peer lending app.
Their excellent record for transparency and favorable loan conditions can yield solid lessons for your app, particularly with regard to trust with clients and communication.
PaySense
PaySense is one of those money-lending apps that specialize in lending personal loans to individuals who may not adhere to the criteria for a traditional loan.
It lends quick, low-value loans with convenient repayment schedules. One nice thing about PaySense is its ease of use—users can request loans, get approved within minutes, and have funds wired into their accounts.
Cash App
Although it started out as a money transfer app, Cash App now offers an assortment of financial services, including instant loans and the ability to buy and sell stocks and Bitcoin.
Cash App is a great example of how to make a complete financial tool in one spot. If you want to implement features like easy money access or a mobile wallet, the Cash App is a great prototype.
SoFi
SoFi is another giant in the online lending market. It provides student loans, personal loans, home loans, and refinancing.
SoFi differs from others in its membership framework, in which borrowers receive access to premium financial planning features, career guidance, and even insurance.
All in all, SoFi is an excellent standard to follow in establishing a more profound connection with your customers than merely lending.
Kiva
Kiva is a non-profit lending platform that centers around microloans for individuals in underserved districts.
It’s actually different from other lending tools on the list in a way it allows people to lend small amounts to entrepreneurs and small business owners in developing countries.
If you consider a more socially mindful approach or want to penetrate the peer-to-peer lending market, Kiva provides an interesting example to turn to.
Affirm
Affirm is a BNPL application that allows consumers to make a buy and pay for it in parts. The application is extremely user-oriented, with freedom regarding when and how to make payments.
If you’re going to provide installment-based loans as part of your application, Affirm is a great representative to emulate insofar as making everything simple and straightforward.
FAQ
- How much does it cost to create a money lending app?
By and large, loan lending app development depends on how much you are willing to spend. For a simple software tool with little functionality, you will probably invest between $20,000–$50,000. An advanced one with credit scoring powered by AI, automation, and extra safety mechanisms ranges from $150,000 and above. Design, platform (iOS, Android, or both), and integrations with third parties also affect the price.
- What features should a loan app have?
At least, your app should include user registration, credit application processing, credit scoring, tracking of repayments, payment integrations, and security mechanisms. To stand out, though, add AI for risk inspection, automated approvals, and customer care chatbots.
- Do I have to adhere to any legal regulations to start a credit app?
Yes! Loan applications involve money and personal data, so you must adhere to financial regulations. In the US, for instance, you must adhere to the Fair Lending Act and California Consumer Privacy Act. In Europe, you must abide by GDPR data protection. Overlooking legal obligations can get your app shut down or fined.
- How do lending apps make money?
The majority of lending applications make revenues from interest on loans, transaction fees, subscription fees, or commissions from collaborations with banks and lenders. Some also offer premium features, such as financial planning or early access to loans, for a fee.