Minimal APIs are an exciting feature introduced in .NET 6, designed to revolutionize how you create APIs.
Imagine building robust APIs with minimal code and zero boilerplate—no more wrestling with controllers, routing, or middleware. That’s what minimal APIs allow you to do. The idea with these APIs is to streamline the development process, making it incredibly easy and efficient.
In this article, we’ll dive into the world of minimal APIs in .NET 8 and guide you through creating a fully functional bookstore API. You’ll learn how to get all books, retrieve a book by its ID, add new books, and even delete books. Let’s get started.
Prerequisites
Before we get going, make sure you have the following prerequisites installed on your machine:
Alternatively, you can use Visual Studio 2022, which comes with built-in support for .NET 8. But in this article, we’ll be using Visual Studio Code. It’s lightweight, easy to use, and cross-platform.
We’ll use Swagger UI to test our API. Swagger UI is a powerful tool that allows you to interact with your API directly from your browser. It provides a user-friendly interface to test your API endpoints, making it easier to test and debug your API.
When you create a new project, it will automatically install the necessary packages and configure the project to use Swagger UI. .NET 8 includes Swagger UI by default, so whether you create your application in Visual Studio or with .NET, Swagger UI will be configured for you.
Run your application, and the Swagger UI will automatically open in your browser – but since we are using VS Code, we need to click on the port number on our terminal.
You can find the source code for this project on GitHub.
Introduction to Minimal APIs
Imagine working in a codebase with numerous endpoints, making it quite large and complex. Traditionally, building an API in ASP.NET Core involves using controllers, routing, middleware, and a significant amount of boilerplate code. But there are two approaches to building an API in ASP.NET Core: the traditional way and the minimal way.
The traditional way is familiar to most developers, involving controllers and extensive infrastructure code. The minimal way, introduced in .NET 6, allows you to create APIs with minimal code and zero boilerplate. This approach simplifies the development process, enabling you to focus on writing business logic rather than dealing with infrastructure code.
Minimal APIs are lightweight, fast, and perfect for building small to medium-sized APIs. They are ideal for prototyping, building microservices, or creating simple APIs that don’t require much complexity. In this handbook, we’ll explore the world of minimal APIs in .NET 6 and learn how to create a fully functional bookstore API from scratch.
How to Create a Minimal API
Creating a minimal API is straightforward when using the dotnet CLI, as the default template is already a minimal API. But if you use Visual Studio, you’ll need to remove the boilerplate code that comes with the project template.
Let’s start by using the dotnet CLI to create a minimal API project.
dotnet new webapi -n BookStoreApi
The dotnet new webapi command creates a new minimal API project named BookStoreApi. This project contains the necessary files and folders to get you started.
Let’s explore the project structure:
-
Program.cs: The entry point of the application, where the host is configured. -
bookapi-minimal.sln: The solution file that contains the project. -
bookapi-minimal.http: A file that contains sample HTTP requests to test the API. -
bookapi-minimal.csproj: The project file that contains the project configuration. -
appsettings.json: The configuration file that stores application settings. -
appsettings.Development.json: The configuration file for the development environment.
When you open the program.cs file, you’ll notice that the code is minimal. The Program.cs file contains the following code:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
var app = builder.Build();
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
var summaries = new[]
{
"Freezing", "Bracing", "Chilly", "Cool", "Mild", "Warm", "Balmy", "Hot", "Sweltering", "Scorching"
};
app.MapGet("/weatherforecast", () =>
{
var forecast = Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index =>
new WeatherForecast
(
DateOnly.FromDateTime(DateTime.Now.AddDays(index)),
Random.Shared.Next(-20, 55),
summaries[Random.Shared.Next(summaries.Length)]
))
.ToArray();
return forecast;
})
.WithName("GetWeatherForecast")
.WithOpenApi();
app.Run();
record WeatherForecast(DateOnly Date, int TemperatureC, string? Summary)
{
public int TemperatureF => 32 + (int)(TemperatureC / 0.5556);
}
If you don’t fully understand the code yet, don’t worry—we’ll cover it in detail in the upcoming sections. The key takeaway is that minimal APIs require very little code, which is one of their main advantages.
The default code sets up a simple weather forecast API that you can use to test your setup. It generates a list of weather forecasts and returns them when you make a GET request to the /weatherforecast endpoint. Also, the code includes Swagger UI to help you test the API.
Pay special attention to the app.MapGet method, which maps a route to a handler function. In this case, it maps the /weatherforecast route to a function that returns a list of weather forecasts. We’ll use similar methods to create our own endpoints in the next sections.
Before we start creating our project folder structure, let’s understand the HTTP methods in both Controller-based and Minimal APIs.
HTTP Methods in Controller-based and Minimal APIs
In a Controller-based approach, which is the traditional way of creating web APIs, you need to create a controller class and define methods for each HTTP method. For example:
-
To create a
GETmethod, you use the[HttpGet]attribute. -
To create a
POSTmethod, you use the[HttpPost]attribute. -
To create a
PUTmethod, you use the[HttpPut]attribute. -
To create a
DELETEmethod, you use the[HttpDelete]attribute.
This is how endpoints are created in a Controller-based approach.
In contrast, Minimal APIs use methods like app.MapGet, app.MapPost, app.MapPut, and app.MapDelete to create endpoints. This is the main difference between the two approaches: Controller-based APIs use attributes to define endpoints, while Minimal APIs use methods.
Now that you understand how to handle HTTP requests in both Controller-based and Minimal APIs, let’s create our project folder structure.
Before we create our project folder structure, let’s first run what we have. As we learned earlier, when you create a project with either Visual Studio or .NET CLI, it comes with a default WeatherForecast project which we can run and see on the UI. Let’s run it to ensure everything works before we go on to create our project folder.
Run this command:
dotnet run
You should see the following output:
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[14]
Now listening on: http://localhost:5228
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Application started. Press Ctrl+C to shut down.
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Hosting environment: Development
info: Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime[0]
Content root path: D:\Devolopemnt\Dotnet\bookapi-minimal
This means the application is running and listening on http://localhost:5228. As I mentioned above, since we are using the dotnet CLI and Visual Studio Code, the application will not automatically open the browser for us. We need to do this manually.
Open your browser and navigate to http://localhost:5228/swagger/index.html to see the default response from the API.
You should see something like this:
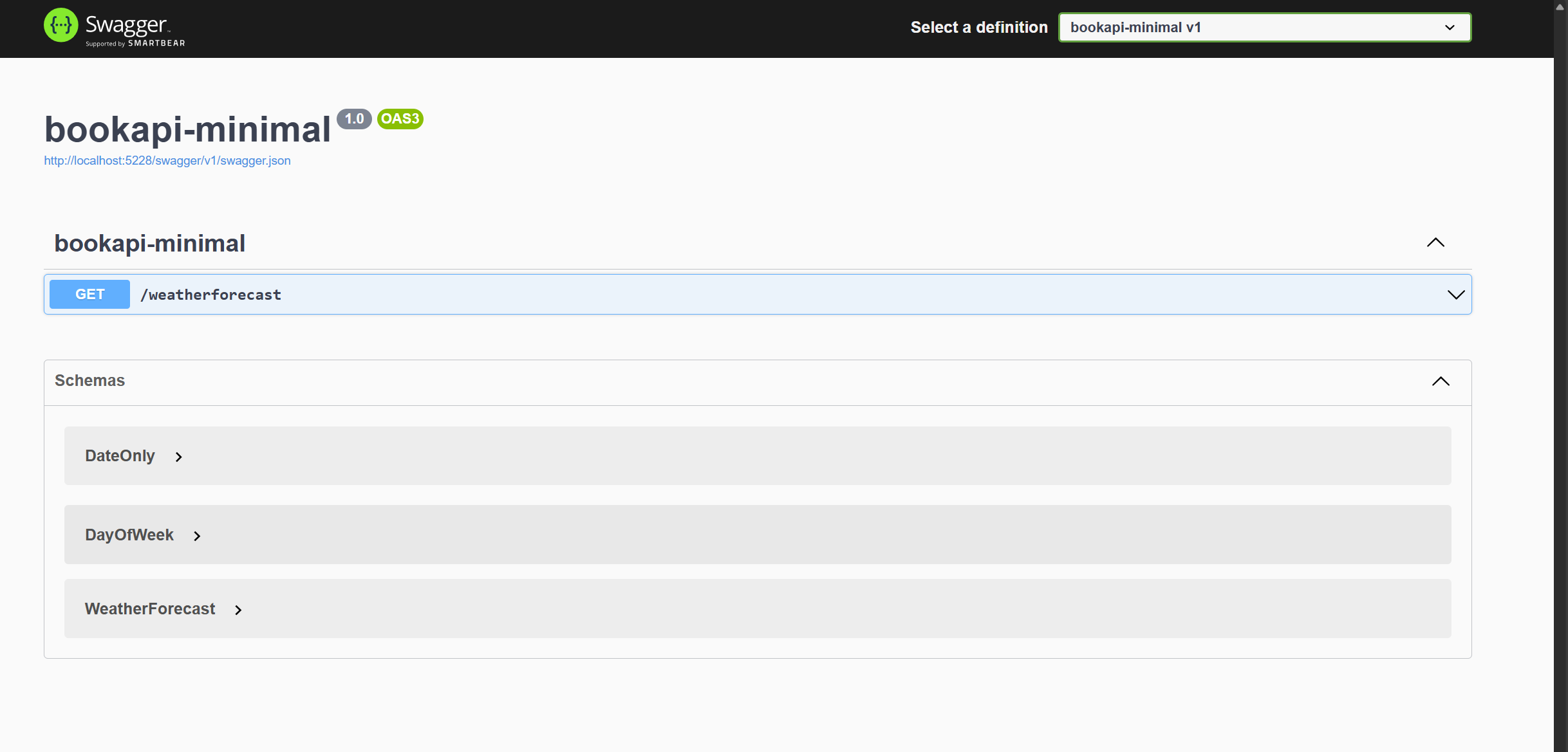
Now the next thing for us to do is find a way to structure our project and create the necessary files and folders to get us started.
Minimal API Project Files
To organize our project, we will create a structured folder hierarchy. This will help keep our code clean and maintainable. Here is the folder structure we will use:
-
AppContext: Contains the database context and related configurations.
-
Configurations: Holds Entity Framework Core configurations and seed data for the database.
-
Contracts: Contains Data Transfer Objects (DTOs) used in our application.
-
Endpoints: Where we define and configure our minimal API endpoints.
-
Exceptions: Contains custom exception classes used in the project.
-
Extensions: Holds extension methods that we will use throughout the project.
-
Models: Contains business logic models.
-
Services: Contains service classes that implement business logic.
-
Interfaces: Holds interface definitions used to map our services.
In Visual Studio Code, you can create this folder structure as follows:
- AppContext
- Configurations
- Contracts
- Endpoints
- Exceptions
- Extensions
- Models
- Services
- Interfaces
After setting up, your project folder structure should look like this:
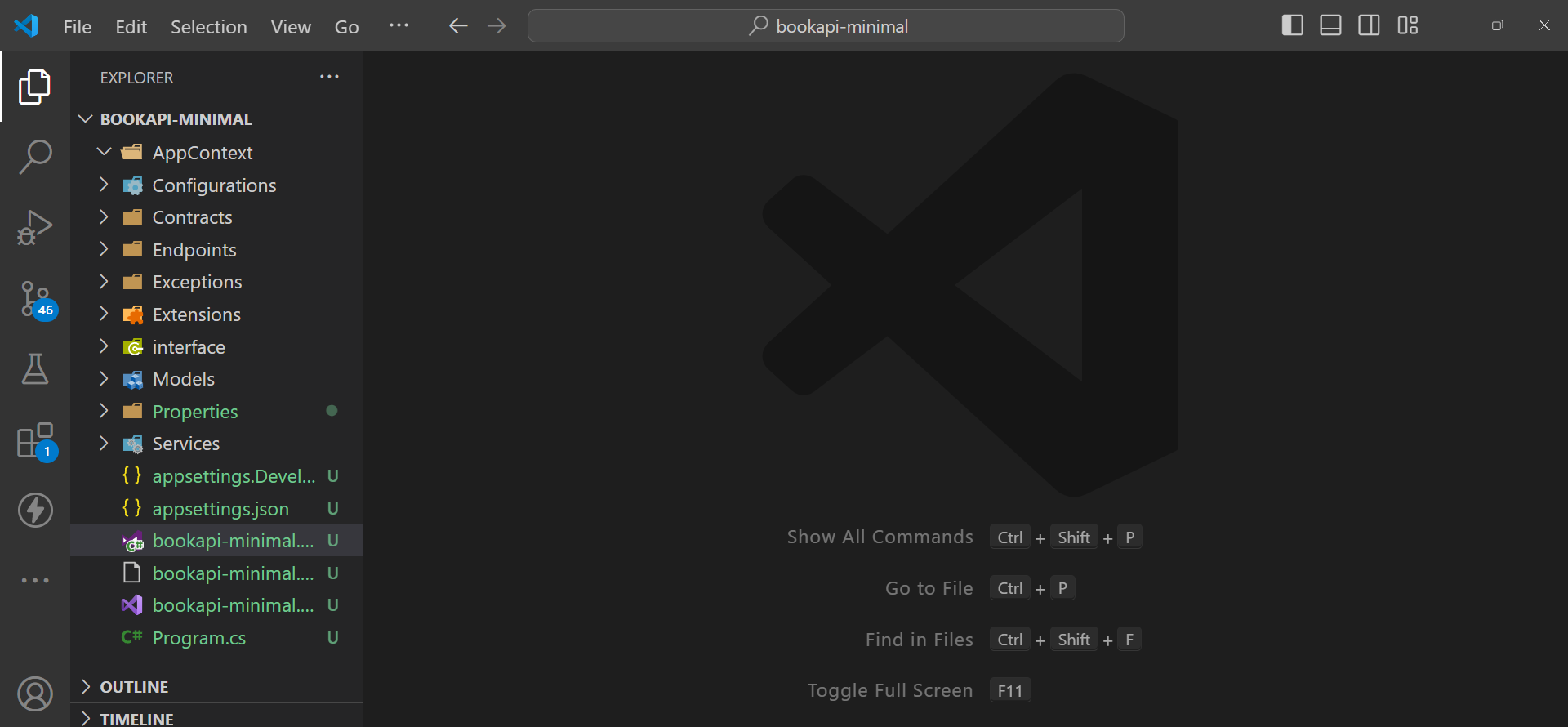
Now that our project Structure is set up we can go ahead and start writing our code. Let’s start by creating our models.
How to Create the Models
In this section, we will create models for our application. Models are the building blocks of our application, representing the data that our application will work with. For our example, we will create a model for a book.
To get started, create a folder named Models in your project directory. Inside this folder, create a file named BookModel.cs and add the following code:
namespace bookapi_minimal.Models
{
public class BookModel
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Author { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public string Category { get; set; }
public string Language { get; set; }
public int TotalPages { get; set; }
}
}
This BookModel class defines the properties that represent the details of a book, such as its title, author, description, category, language, and total pages. Each property is designed to hold specific information about the book, making it easy to manage and manipulate book data within our application.
Now that we have created our model, let’s create our database context.
How to Create the Database Context
The database context is a class that represents a session with the database. It’s responsible for interacting with the database and executing database operations. In our application, we will use Entity Framework Core to interact with our database.
Install the Required Packages
Before creating our database context, we need to install the following packages:
You can install these packages using the following commands:
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
dotnet add package FluentValidation.DependencyInjectionExtensions
Verify Package Installation
To verify that the packages are installed, open the bookapi-minimal.csproj file in your project’s root directory. You should see the installed packages listed as follows:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Web">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>net8.0</TargetFramework>
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
<ImplicitUsings>enable</ImplicitUsings>
<RootNamespace>bookapi_minimal</RootNamespace>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="FluentValidation.DependencyInjectionExtensions" Version="11.9.2" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.OpenApi" Version="8.0.6" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore" Version="8.0.8" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design" Version="8.0.8">
<IncludeAssets>runtime; build; native; contentfiles; analyzers; buildtransitive</IncludeAssets>
<PrivateAssets>all</PrivateAssets>
</PackageReference>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer" Version="8.0.8" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools" Version="8.0.8">
<IncludeAssets>runtime; build; native; contentfiles; analyzers; buildtransitive</IncludeAssets>
<PrivateAssets>all</PrivateAssets>
</PackageReference>
<PackageReference Include="Swashbuckle.AspNetCore" Version="6.4.0" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
This confirms that the packages have been successfully installed.
Now let’s create our database context.
In the AppContext folder, create a new file named ApplicationContext.cs and add the following code:
using bookapi_minimal.Models;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace bookapi_minimal.AppContext
{
public class ApplicationContext(DbContextOptions<ApplicationContext> options) : DbContext(options)
{
private const string DefaultSchema = "bookapi";
public DbSet<BookModel> Books { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
modelBuilder.HasDefaultSchema(DefaultSchema);
modelBuilder.ApplyConfigurationsFromAssembly(typeof(ApplicationContext).Assembly);
modelBuilder.ApplyConfigurationsFromAssembly(typeof(ApplicationContext).Assembly);
}
}
}
Let’s break down the code above:
-
We define a class named
ApplicationContextthat inherits fromDbContext. TheDbContextclass is part of Entity Framework Core and represents a session with the database. -
The constructor accepts an instance of
DbContextOptions<ApplicationContext>. This constructor is used to configure the database context options. -
We define a property named
BookstypeDbSet<BookModel>. This property represents the collection of books in our database. -
We override the
OnModelCreatingmethod to configure the database schema and apply any configurations defined in our application.
Now that we have created our database context, let’s create our extension method and register our database context in the dependency injection container.
Create an Extension Method
Before we create the extension method, let’s understand what an extension method is in the context of ASP.NET Core.
An extension method is a static method that adds new functionality to an existing type without modifying the original type. In ASP.NET Core, extension methods are commonly used to extend the functionality of the IServiceCollection interface, which is used to register services in the dependency injection container.
Services are components that provide functionality to an application, such as database access, logging, and configuration. By creating an extension method for the IServiceCollection interface, you can simplify the process of registering your services in the dependency injection container.
Instead of putting everything in the Program.cs file, we will create an extension method to register our services in the dependency injection container. This will help us keep our code clean and organized.
In the Extensions folder, create a new file named ServiceExtensions.cs and add the following code:
using System.Reflection;
using bookapi_minimal.AppContext;
using FluentValidation;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace bookapi_minimal.Extensions
{
public static class ServiceExtensions
{
public static void AddApplicationServices(this IHostApplicationBuilder builder)
{
if (builder == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(builder));
if (builder.Configuration == null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(builder.Configuration));
builder.Services.AddDbContext<ApplicationContext>(configure =>
{
configure.UseSqlServer(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("sqlConnection"));
});
builder.Services.AddValidatorsFromAssembly(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly());
}
}
}
Let’s break down the code above:
-
We define a static class named
ServiceExtensionsthat contains an extension method namedAddApplicationServices. This method extends theIHostApplicationBuilderinterface, which is used to configure the application’s request processing pipeline. -
The
AddApplicationServicesmethod accepts an instance ofIHostApplicationBuilderas a parameter. This parameter is used to access the application’s configuration and services. -
We add the
ApplicationContextto the dependency injection container and configure it to use SQL Server as the database provider. We retrieve the connection string from theappsettings.jsonfile using theGetConnectionStringmethod. -
We add
validatorsfrom the currentassemblyusing theAddValidatorsFromAssemblymethod. This method scans the current assembly for classes that implement the IValidator interface and registers them in the dependency injection container.
Next, we need to add the connection string to the appsettings.json file. Add the following code to your appsettings.json file:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"sqlConnection": "Server=localhost\\SQLEXPRESS02;Database=BookAPIMinimalAPI;Integrated Security=true;TrustServerCertificate=true;"
}
}
Make sure to replace your_password it with your actual SQL Server password.
Your appsettings.json file should look like this:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"ConnectionStrings": {
"sqlConnection": "Server=localhost\\SQLEXPRESS02;Database=BookAPIMinimalAPI;Integrated Security=true;TrustServerCertificate=true;"
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}
Congratulations! You have successfully created the database context, extension method, and connection string for your application. In the next section, we will create a Contract.
How to Create a Contract
Contracts are Data Transfer Objects (DTOs) that define the structure of the data exchanged between the client and the server. In our application, we will create contracts to represent the data sent and received by our API endpoints.
Here are the contracts we are going to create:
-
CreateBookRequest: This represents the data sent when creating a new book.
-
UpdateBookRequest: tHI Represents the data sent when updating an existing book.
-
BookResponse: Represents the data returned when retrieving a book.
-
ErrorResponse: Represents the error response returned when an exception occurs.
-
ApiResponse: Represents the response returned by the API.
In the Contracts folder, create a new file named CreateBookRequest and add the following code:
namespace bookapi_minimal.Contracts
{
public record CreateBookRequest
{
public string Title { get; init; }
public string Author { get; init; }
public string Description { get; init; }
public string Category { get; init; }
public string Language { get; init; }
public int TotalPages { get; init; }
}
}
In the Contracts folder, create a new file named UpdateBookRequest and add the following code:
namespace bookapi_minimal.Contracts
{
public record UpdateBookRequest
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Author { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public string Category { get; set; }
public string Language { get; set; }
public int TotalPages { get; set; }
}
}
In the Contracts folder, create a new file named BookResponse and add the following code:
namespace bookapi_minimal.Contracts
{
public record BookResponse
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Author { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public string Category { get; set; }
public string Language { get; set; }
public int TotalPages { get; set; }
}
}
In the Contracts folder, create a new file named ErrorResponse and add the following code:
namespace bookapi_minimal.Contracts
{
public record ErrorResponse
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public int StatusCode { get; set; }
public string Message { get; set; }
}
}
In the Contracts folder, create a new file named ApiResponse and add the following code:
namespace bookapi_minimal.Contracts
{
public class ApiResponse<T>
{
public T Data { get; set; }
public string Message { get; set; }
public ApiResponse(T data, string message)
{
Data = data;
Message = message;
}
}
}
These contracts help us define the structure of the data exchanged between the client and the server, making it easier to work with the data in our application.
In the next section, we will create services to implement the business logic of our application.
How to Add Services
Services are components that provide functionality to an application. In our application, we will create services to implement the business logic of our application. We will create services to handle CRUD operations for books, validate book data, and handle exceptions.
In ASP.NET Core, services are registered in the dependency injection container and can be injected into other components, such as controllers and endpoints, But this is a minimal API so we will inject the services directly into the endpoints.
Let’s create an interface for our services. In the Interfaces folder, create a new file named IBookService.cs and add the following code:
using bookapi_minimal.Contracts;
namespace bookapi_minimal.Interfaces
{
public interface IBookService
{
Task<BookResponse> AddBookAsync(CreateBookRequest createBookRequest);
Task<BookResponse> GetBookByIdAsync(Guid id);
Task<IEnumerable<BookResponse>> GetBooksAsync();
Task<BookResponse> UpdateBookAsync(Guid id, UpdateBookRequest updateBookRequest);
Task<bool> DeleteBookAsync(Guid id);
}
}
Let’s break down the code above: We have defined an interface named IBookService that contains methods to handle CRUD operations for books. The interface defines the following methods:
-
AddBookAsync: Adds a new book to the database. -
GetBookByIdAsync: Retrieves a book by its ID. -
GetBooksAsync: Retrieves all books from the database. -
UpdateBookAsync: Updates an existing book.
We are using the Contract we created earlier in the Contracts folder. The IBookService interface defines the structure of the methods that will be implemented by the service classes. This helps us separate the interface from the implementation, making it easier to maintain and test our code.
Now that we have created the interface, let’s create the service class that implements the interface.
How to Implement the Book Service
This service will implement the IBookService interface and provide the business logic for our application. In the Services folder, create a new file named BookService.cs . Your initial file should look like this:
namespace bookapi_minimal.Services
{
public class BookService
{
}
}
The first thing we need to do is add the interface to the BookService class. Update the BookService class to implement the IBookService interface as follows:
using bookapi_minimal.Interfaces;
namespace bookapi_minimal.Services
{
public class BookService:IBookService
{
}
}
When you do this, your VS Code might show an error because we have not implemented the methods in the interface. Let’s go ahead and implement the methods in the BookService class.
In VS Code you can use the Ctrl + . shortcut to implement the methods in the interface. Then you will see the following code generated for you:
using bookapi_minimal.Contracts;
using bookapi_minimal.Interfaces;
namespace bookapi_minimal.Services
{
public class BookService : IBookService
{
public Task<BookResponse> AddBookAsync(CreateBookRequest createBookRequest)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Task<bool> DeleteBookAsync(Guid id)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Task<BookResponse> GetBookByIdAsync(Guid id)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Task<IEnumerable<BookResponse>> GetBooksAsync()
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Task<BookResponse> UpdateBookAsync(Guid id, UpdateBookRequest updateBookRequest)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
}
Now you can see that the methods in the interface have been implemented in the BookService class. We will implement the business logic for each method in the next section.
Before we do that, let’s add the necessary dependencies to the BookService class. We need to inject the ApplicationContext and ILogger dependencies into the BookService class. ApplicationContext is used to interact with the database, while ILogger is used for logging.
To inject the dependencies, update the BookService class as follows:
private readonly ApplicationContext _context;
private readonly ILogger<BookService> _logger;
Since we have added the dependencies, we need to update the BookService constructor to accept the dependencies. Update the BookService constructor as follows:
public BookService(ApplicationContext context, ILogger<BookService> logger)
{
_context = context;
_logger = logger;
}
Now that we have added the dependencies and updated the constructor, we can implement the business logic for each method in the BookService class.
Let’s create logic for the CREATE, READ, UPDATE, and DELETE operations in the BookService class.
How to Implement the AddBookAsync Method
As I mentioned earlier, we’ll use the AddBookAsync method to add a new book to the database. In this method, we will create a new book entity, map the data from the CreateBookRequest object to the book entity, and save the book entity to the database. We will also return the book entity as an BookResponse object.
Update the AddBookAsync method in the BookService class as follows:
public async Task<BookResponse> AddBookAsync(CreateBookRequest createBookRequest)
{
try
{
var book = new BookModel
{
Title = createBookRequest.Title,
Author = createBookRequest.Author,
Description = createBookRequest.Description,
Category = createBookRequest.Category,
Language = createBookRequest.Language,
TotalPages = createBookRequest.TotalPages
};
_context.Books.Add(book);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
_logger.LogInformation("Book added successfully.");
return new BookResponse
{
Id = book.Id,
Title = book.Title,
Author = book.Author,
Description = book.Description,
Category = book.Category,
Language = book.Language,
TotalPages = book.TotalPages
};
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Error adding book: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}
In this code, we are creating a new book entity from the CreateBookRequest object, mapping the data from the CreateBookRequest object to the book entity, saving the book entity to the database, and returning the book entity as a BookResponse object.
We are also logging information and errors using the ILogger dependency. If an exception occurs during the process, we log the error message and rethrow the exception.
Now that we have implemented the AddBookAsync method, let’s implement the GetBookByIdAsync method.
How to Implement the GetBookByIdAsync Method
The GetBookByIdAsync method is used to retrieve a book by its ID from the database. In this method, we will query the database for the book with the specified ID, map the book entity to a BookResponse object, and return the BookResponse object.
Update the GetBookByIdAsync method in the BookService class as follows:
public async Task<BookResponse> GetBookByIdAsync(Guid id)
{
try
{
var book = await _context.Books.FindAsync(id);
if (book == null)
{
_logger.LogWarning($"Book with ID {id} not found.");
return null;
}
return new BookResponse
{
Id = book.Id,
Title = book.Title,
Author = book.Author,
Description = book.Description,
Category = book.Category,
Language = book.Language,
TotalPages = book.TotalPages
};
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Error retrieving book: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}
In this code, we are querying the database for the book with the specified ID, mapping the book entity to a BookResponse object, and returning the BookResponse object. We are also logging information and errors using the ILogger dependency.
If the book with the specified ID is not found, we log a warning message and return null. If an exception occurs during the process, we log the error message and rethrow the exception.
Now that we have implemented the GetBookByIdAsync method, let’s implement the GetBooksAsync method.
How to Implement the GetBooksAsync Method
The GetBooksAsync method is used to retrieve all books from the database. In this method, we will query the database for all books, map each book entity to a BookResponse object, and return a list of BookResponse objects.
Update the GetBooksAsync method in the BookService class as follows:
public async Task<IEnumerable<BookResponse>> GetBooksAsync()
{
try
{
var books = await _context.Books.ToListAsync();
return books.Select(book => new BookResponse
{
Id = book.Id,
Title = book.Title,
Author = book.Author,
Description = book.Description,
Category = book.Category,
Language = book.Language,
TotalPages = book.TotalPages
});
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Error retrieving books: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}
Here, we are querying the database for all books, mapping each book entity to an BookResponse object, and returning a list of BookResponse objects. We are also logging information and errors using the ILogger dependency. If an exception occurs during the process, we log the error message and rethrow the exception.
Now that we have implemented the GetBooksAsync method, let’s implement the UpdateBookAsync method.
How to Implement the UpdateBookAsync Method
The UpdateBookAsync method is used to update an existing book in the database. In this method, we will query the database for the book with the specified ID, update the book entity with the data from the UpdateBookRequest object, save the updated book entity to the database, and return the updated book entity as a BookResponse object.
Update the UpdateBookAsync method in the BookService class as follows:
public async Task<BookResponse> UpdateBookAsync(Guid id, UpdateBookRequest book)
{
try
{
var existingBook = await _context.Books.FindAsync(id);
if (existingBook == null)
{
_logger.LogWarning($"Book with ID {id} not found.");
return null;
}
existingBook.Title = book.Title;
existingBook.Author = book.Author;
existingBook.Description = book.Description;
existingBook.Category = book.Category;
existingBook.Language = book.Language;
existingBook.TotalPages = book.TotalPages;
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
_logger.LogInformation("Book updated successfully.");
return new BookResponse
{
Id = existingBook.Id,
Title = existingBook.Title,
Author = existingBook.Author,
Description = existingBook.Description,
Category = existingBook.Category,
Language = existingBook.Language,
TotalPages = existingBook.TotalPages
};
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Error updating book: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}
Here, we are querying the database for the book with the specified ID, updating the book entity with the data from the UpdateBookRequest object, saving the updated book entity to the database, and returning the updated book entity as a BookResponse object. We are also logging information and errors using the ILogger dependency.
If the book with the specified ID is not found, we log a warning message and return null. If an exception occurs during the process, we log the error message and rethrow the exception.
Now that we have implemented the UpdateBookAsync method, let’s implement the DeleteBookAsync method.
How to Implement the DeleteBookAsync Method
The DeleteBookAsync method is used to delete an existing book from the database. In this method, we will query the database for the book with the specified ID, remove the book entity from the database, and return a boolean value indicating whether the book was successfully deleted.
Update the DeleteBookAsync method in the BookService class as follows:
public async Task<bool> DeleteBookAsync(Guid id)
{
try
{
var book = await _context.Books.FindAsync(id);
if (book == null)
{
_logger.LogWarning($"Book with ID {id} not found.");
return false;
}
_context.Books.Remove(book);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
_logger.LogInformation($"Book with ID {id} deleted successfully.");
return true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Error deleting book: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}
In this code, we are querying the database for the book with the specified ID, removing the book entity from the database, and returning a boolean value indicating whether the book was successfully deleted. We are also logging information and errors using the ILogger dependency.
If the book with the specified ID is not found, we log a warning message and return false. If an exception occurs during the process, we log the error message and rethrow the exception.
Now you have successfully implemented the business logic for the AddBookAsync, GetBookByIdAsync, GetBooksAsync, UpdateBookAsync, and DeleteBookAsync methods in the BookService class. These methods handle the CRUD operations for books, validate book data, and handle exceptions. By now, your BookService class should look like this:
using bookapi_minimal.AppContext;
using bookapi_minimal.Contracts;
using bookapi_minimal.Interfaces;
using bookapi_minimal.Models;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace bookapi_minimal.Services
{
public class BookService : IBookService
{
private readonly ApplicationContext _context;
private readonly ILogger<BookService> _logger;
public BookService(ApplicationContext context, ILogger<BookService> logger)
{
_context = context;
_logger = logger;
}
public async Task<BookResponse> AddBookAsync(CreateBookRequest createBookRequest)
{
try
{
var book = new BookModel
{
Title = createBookRequest.Title,
Author = createBookRequest.Author,
Description = createBookRequest.Description,
Category = createBookRequest.Category,
Language = createBookRequest.Language,
TotalPages = createBookRequest.TotalPages
};
_context.Books.Add(book);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
_logger.LogInformation("Book added successfully.");
return new BookResponse
{
Id = book.Id,
Title = book.Title,
Author = book.Author,
Description = book.Description,
Category = book.Category,
Language = book.Language,
TotalPages = book.TotalPages
};
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Error adding book: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}
public async Task<BookResponse> GetBookByIdAsync(Guid id)
{
try
{
var book = await _context.Books.FindAsync(id);
if (book == null)
{
_logger.LogWarning($"Book with ID {id} not found.");
return null;
}
return new BookResponse
{
Id = book.Id,
Title = book.Title,
Author = book.Author,
Description = book.Description,
Category = book.Category,
Language = book.Language,
TotalPages = book.TotalPages
};
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Error retrieving book: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}
public async Task<IEnumerable<BookResponse>> GetBooksAsync()
{
try
{
var books = await _context.Books.ToListAsync();
return books.Select(book => new BookResponse
{
Id = book.Id,
Title = book.Title,
Author = book.Author,
Description = book.Description,
Category = book.Category,
Language = book.Language,
TotalPages = book.TotalPages
});
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Error retrieving books: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}
public async Task<BookResponse> UpdateBookAsync(Guid id, UpdateBookRequest book)
{
try
{
var existingBook = await _context.Books.FindAsync(id);
if (existingBook == null)
{
_logger.LogWarning($"Book with ID {id} not found.");
return null;
}
existingBook.Title = book.Title;
existingBook.Author = book.Author;
existingBook.Description = book.Description;
existingBook.Category = book.Category;
existingBook.Language = book.Language;
existingBook.TotalPages = book.TotalPages;
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
_logger.LogInformation("Book updated successfully.");
return new BookResponse
{
Id = existingBook.Id,
Title = existingBook.Title,
Author = existingBook.Author,
Description = existingBook.Description,
Category = existingBook.Category,
Language = existingBook.Language,
TotalPages = existingBook.TotalPages
};
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Error updating book: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}
public async Task<bool> DeleteBookAsync(Guid id)
{
try
{
var book = await _context.Books.FindAsync(id);
if (book == null)
{
_logger.LogWarning($"Book with ID {id} not found.");
return false;
}
_context.Books.Remove(book);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
_logger.LogInformation($"Book with ID {id} deleted successfully.");
return true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError($"Error deleting book: {ex.Message}");
throw;
}
}
}
}
Congratulations! You have successfully implemented the business logic for the AddBookAsync, GetBookByIdAsync, GetBooksAsync, UpdateBookAsync, and DeleteBookAsync methods in the BookService class.
There’s one thing we need to do: we need to register the service in our extension method. Let’s go ahead and do that.
In your ServiceExtensions.cs file, add the following code:
builder.Services.AddScoped<IBookService, BookService>();
This will register the BookService class as a scoped service. This means that the service will be created once per request and disposed of after the request is complete.
Now that we have the service working, let’s go ahead and create the exception classes.
How to Create Exceptions
Properly handling exceptions is crucial for ensuring the stability and reliability of an application. In the context of ASP.NET Core, there are two main types of exceptions:
-
System Exceptions: These are exceptions thrown by the .NET runtime or the underlying system.
-
Application Exceptions: These are exceptions thrown by the application code to handle specific errors or conditions.
In ASP.NET Core with .NET 8, a new feature called global exception handling was introduced. This feature allows you to handle exceptions globally in your application, making it easier to manage errors and provide a consistent user experience.
In our application, we will create custom exception classes to handle specific errors and conditions. We’ll also leverage the global exception handling feature to manage exceptions globally, ensuring a uniform approach to error handling across the entire application.
We are going to create the following exception classes:
-
NoBookFoundException: Thrown when a book with the specified ID is not found. -
BookDoesNotExistException: Thrown when a book with the specified ID does not exist. -
GlobalExceptionHandler: Handles exceptions globally in the application.
In the Exceptions folder, create a new file named NoBookFoundException.cs and add the following code:
namespace bookapi_minimal.Exceptions
{
public class NoBookFoundException : Exception
{
public NoBookFoundException() : base("No books found")
{}
}
}
In this code, we are creating a custom exception class named NoBookFoundException that inherits from the Exception class. The NoBookFoundException class is used to handle the scenario where no books are found in the database. We are also providing a custom error message for the exception.
In the Exceptions folder, create a new file named BookDoesNotExistException.cs and add the following code:
namespace bookapi_minimal.Exceptions
{
public class BookDoesNotExistException : Exception
{
private int id { get; set; }
public BookDoesNotExistException(int id) : base($"Book with id {id} does not exist")
{
this.id = id;
}
}
}
In this code, we are creating a custom exception class named BookDoesNotExistException that inherits from the Exception class. The BookDoesNotExistException class is used to handle the scenario where a book with the specified ID does not exist in the database. We are also providing a custom error message for the exception.
In the Exceptions folder, create a new file named GlobalExceptionHandler.cs and add the following code:
using System.Net;
using bookapi_minimal.Contracts;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics;
namespace bookapi_minimal.Exceptions
{
public class GlobalExceptionHandler : IExceptionHandler
{
private readonly ILogger<GlobalExceptionHandler> _logger;
public GlobalExceptionHandler(ILogger<GlobalExceptionHandler> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public async ValueTask<bool> TryHandleAsync(
HttpContext httpContext,
Exception exception,
CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
_logger.LogError(exception, "An error occurred while processing your request");
var errorResponse = new ErrorResponse
{
Message = exception.Message,
Title = exception.GetType().Name
};
switch (exception)
{
case BadHttpRequestException:
errorResponse.StatusCode = (int)HttpStatusCode.BadRequest;
break;
case NoBookFoundException:
case BookDoesNotExistException:
errorResponse.StatusCode = (int)HttpStatusCode.NotFound;
break;
default:
errorResponse.StatusCode = (int)HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError;
break;
}
httpContext.Response.StatusCode = errorResponse.StatusCode;
await httpContext.Response.WriteAsJsonAsync(errorResponse, cancellationToken);
return true;
}
}
}
Let’s break down the code above:
-
We define a class named
GlobalExceptionHandlerthat implements theIExceptionHandlerinterface. TheIExceptionHandlerinterface is used to handle exceptions globally in the application. -
The
GlobalExceptionHandlerclass contains a constructor that initializes theILogger<GlobalExceptionHandler>dependency. TheILoggeris used for logging information and errors. -
The
TryHandleAsyncmethod is used to handle exceptions asynchronously. This method accepts theHttpContext,Exception, andCancellationTokenas parameters. -
We log the exception details using the
ILoggerdependency. -
We create an
ErrorResponseobject to represent the error response returned by the API. TheErrorResponseobject contains the error message, title, and status code. -
We determine the status code based on the type of exception. If the exception is a
BadHttpRequestException, we set the status code toBadRequest. If the exception is aNoBookFoundExceptionorBookDoesNotExistException, we set the status code toNotFound. Otherwise, we set the status code toInternalServerError. -
We set the response status code using the
httpContext.Response.StatusCodeproperty. -
We write the error response as JSON using the
httpContext.Response.WriteAsJsonAsyncmethod. -
We return
trueto indicate that the exception was handled successfully.
Now that we have created the exception classes, let’s register the GlobalExceptionHandler in the dependency injection container. Since we created an Extension method for registering services in the dependency injection container, we will add the GlobalExceptionHandler to the ServiceExtensions class.
Update the ServiceExtensions class in the Extensions folder as follows:
builder.Services.AddExceptionHandler<GlobalExceptionHandler>();
builder.Services.AddProblemDetails();
The AddExceptionHandler method registers the GlobalExceptionHandler in the dependency injection container. The AddProblemDetails method registers the ProblemDetails class in the dependency injection container.
Now that we have registered the GlobalExceptionHandler in the dependency injection container, we can use it to handle exceptions globally in our application. In the next section, we will create the API endpoints to interact with the book data.
How to Create the API Endpoints
In the context of minimal APIs in ASP.NET Core, there are many ways to set up your endpoints.
You can define them directly in your Program.cs file. But as your project grows and you need to add more endpoints or functionality, it’s helpful to organize your code better. One way to achieve this is by creating a separate class to handle all the endpoints.
As we’ve discussed above, minimal APIs don’t use controllers or views like traditional ASP.NET Core applications. Instead, they use methods such as MapGet, MapPost, MapPut, and MapDelete to define HTTP methods and routes for API endpoints.
To get started, navigate to the Endpoints folder and create a new file named BookEndpoints.cs. Add the following code to the file:
namespace bookapi_minimal.Endpoints
{
public static class BookEndPoint
{
public static IEndpointRouteBuilder MapBookEndPoint(this IEndpointRouteBuilder app)
{
return app;
}
}
}
The BookEndpoints class contains a MapBookEndPoint method that returns an IEndpointRouteBuilder object. The IEndpointRouteBuilder object is used to define the HTTP methods and routes for the API endpoints. In the next sections, we will define the API endpoints for creating, reading, updating, and deleting books.
How to Create the AddBookAsync Books Endpoint
In this section, we will create the AddBookAsync endpoint. This endpoint will accept a Book object as a JSON payload and add it to the database. We will use the MapPost method to define the HTTP method and route for this endpoint.
Add the following code to the BookEndpoints class:
app.MapPost("/books", async (CreateBookRequest createBookRequest, IBookService bookService) =>
{
var result = await bookService.AddBookAsync(createBookRequest);
return Results.Created($"/books/{result.Id}", result);
});
-
Route Definition: The MapPost method defines the route for the endpoint as
/books. -
Request Model: The endpoint accepts an
CreateBookRequestobject as a JSON payload. TheCreateBookRequestobject contains the data required to create a new book. -
Response Model: The endpoint returns a
Bookobject as a JSON payload. TheBookobject contains the data for the newly created book. -
Return Value: The endpoint returns a
Createdresult. TheCreatedresult contains the location of the newly created book and theBookobject.
How to Create the GetBookAsync Book Endpoint
In this section, we will create the GetBookAsync endpoint. This endpoint will accept a book ID as a query parameter and return the book with the specified ID. We will use the MapGet method to define the HTTP method and route for this endpoint.
Add the following code to the BookEndpoints class:
app.MapGet("/books", async (IBookService bookService) =>
{
var result = await bookService.GetBooksAsync();
return Results.Ok(result);
});
-
Route Definition: The MapGet method defines the route for the endpoint as
/books. -
Request Model: The endpoint accepts a
Bookobject as a JSON payload. TheBookobject contains the data required to create a new book. -
Response Model: The endpoint returns a
Bookobject as a JSON payload. TheBookobject contains the data for the newly created book. -
Return Value: The endpoint returns an
Okresult. TheOkresult contains theBookobject.
How to Create the GetBookByIdAsync Book Endpoint
In this section, we will create the GetBookByIdAsync endpoint. This endpoint will accept a book ID as a route parameter and return the book with the specified ID. We will use the MapGet method to define the HTTP method and route for this endpoint.
Add the following code to the BookEndpoints class:
app.MapGet("/books/{id:guid}", async (Guid id, IBookService bookService) =>
{
var result = await bookService.GetBookByIdAsync(id);
return result != null ? Results.Ok(result) : Results.NotFound();
});
-
Route Definition: The MapGet method defines the route for the endpoint as
/books/{id:guid}. The{id:guid}parameter specifies that theidparameter should be a GUID. -
Request Model: The endpoint accepts a
Bookobject as a JSON payload. TheBookobject contains the data required to create a new book. -
Response Model: The endpoint returns a
Bookobject as a JSON payload. TheBookobject contains the data for the newly created book. -
Return Value: The endpoint returns an
Okresult if the book is found. TheNotFoundresult is returned if the book is not found.
How to Create the UpdateBookAsync Book Endpoint
In this section, we will create the UpdateBookAsync endpoint. This endpoint will accept a book ID as a route parameter and an Book object as a JSON payload and update the book with the specified ID. We will use the MapPut method to define the HTTP method and route for this endpoint.
Add the following code to the BookEndpoints class:
app.MapPut("/books/{id:guid}", async (Guid id, UpdateBookRequest updateBookRequest, IBookService bookService) =>
{
var result = await bookService.UpdateBookAsync(id, updateBookRequest);
return result != null ? Results.Ok(result) : Results.NotFound();
});
-
Route Definition: The MapPut method defines the route for the endpoint as
/books/{id:guid}. The{id:guid}parameter specifies that theidparameter should be a GUID. -
Request Model: The endpoint accepts a
Bookobject as a JSON payload. TheBookobject contains the data required to create a new book. -
Response Model: The endpoint returns a
Bookobject as a JSON payload. TheBookobject contains the data for the newly created book. -
Return Value: The endpoint returns an
Okresult if the book is found. TheNotFoundresult is returned if the book is not found.
How to Create the DeleteBookAsync Book Endpoint
In this section, we will create the DeleteBookAsync endpoint. This endpoint will accept a book ID as a route parameter and delete the book with the specified ID. We will use the MapDelete method to define the HTTP method and route for this endpoint.
Add the following code to the BookEndpoints class:
app.MapDelete("/books/{id:guid}", async (Guid id, IBookService bookService) =>
{
var result = await bookService.DeleteBookAsync(id);
return result ? Results.NoContent() : Results.NotFound();
});
-
Route Definition: The MapDelete method defines the route for the endpoint as
/books/{id:guid}. The{id:guid}parameter specifies that theidparameter should be a GUID. -
Request Model: The endpoint accepts a
Bookobject as a JSON payload. TheBookobject contains the data required to create a new book. -
Response Model: The endpoint returns a
Bookobject as a JSON payload. TheBookobject contains the data for the newly created book. -
Return Value: The endpoint returns a
NoContentresult if the book is deleted successfully. TheNotFoundresult is returned if the book is not found.
Now we have defined all the methods for the book endpoints. So your endpoint class should look like this:
using bookapi_minimal.Contracts;
using bookapi_minimal.Interfaces;
namespace bookapi_minimal.Endpoints
{
public static class BookEndPoint
{
public static IEndpointRouteBuilder MapBookEndPoint(this IEndpointRouteBuilder app)
{
app.MapPost("/books", async (CreateBookRequest createBookRequest, IBookService bookService) =>
{
var result = await bookService.AddBookAsync(createBookRequest);
return Results.Created($"/books/{result.Id}", result);
});
app.MapGet("/books", async (IBookService bookService) =>
{
var result = await bookService.GetBooksAsync();
return Results.Ok(result);
});
app.MapGet("/books/{id:guid}", async (Guid id, IBookService bookService) =>
{
var result = await bookService.GetBookByIdAsync(id);
return result != null ? Results.Ok(result) : Results.NotFound();
});
app.MapPut("/books/{id:guid}", async (Guid id, UpdateBookRequest updateBookRequest, IBookService bookService) =>
{
var result = await bookService.UpdateBookAsync(id, updateBookRequest);
return result != null ? Results.Ok(result) : Results.NotFound();
});
app.MapDelete("/books/{id:guid}", async (Guid id, IBookService bookService) =>
{
var result = await bookService.DeleteBookAsync(id);
return result ? Results.NoContent() : Results.NotFound();
});
return app;
}
}
}
Congratulations! You have created all the endpoints for the book API. The endpoints handle the CRUD operations for books and return the appropriate responses based on the request and data.
How to Register the Endpoints
After defining the API endpoints for the book API, the next step is to register these endpoints in the Program.cs file. We will use the MapBookEndpoints method to register the book endpoints.
We should also clean up our Program.cs class to ensure it remains organized and maintainable.
using System.Reflection;
using bookapi_minimal.Endpoints;
using bookapi_minimal.Services;
using Microsoft.OpenApi.Models;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.AddApplicationServices();
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen(c=>
{
c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new OpenApiInfo { Title = "Mimal API", Version = "v1", Description = "Showing how you can build minimal " +
"api with .net" });
var xmlFile = $"{Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Name}.xml";
var xmlPath = Path.Combine(AppContext.BaseDirectory, xmlFile);
c.IncludeXmlComments(xmlPath);
});
var app = builder.Build();
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseExceptionHandler();
app.MapGroup("/api/v1/")
.WithTags(" Book endpoints")
.MapBookEndPoint();
app.Run();
Let’s break down the key components of the Program.cs file:
-
AddApplicationServices: This method registers the necessary services for the API. It is an extension method we created earlier to add services to the dependency injection container.
-
AddSwaggerGen: This method registers the Swagger generator, which is used to create the Swagger documentation for the API. We specify the title, version, and description of the API in the Swagger document.
-
MapGroup: This method groups the endpoints. It takes a path as a parameter and returns an
IEndpointRouteBuilderobject. We use theWithTagsmethod to add tags to the endpoints and theMapBookEndpointsmethod to register the book endpoints. -
Run: This method starts the application.
To enable Swagger documentation, you need to add the GenerateDocumentationFile property to your .csproj file. In this example, the file is named bookapi-minimal.csproj, but the name may vary based on your project.
Add the following line to your .csproj file:
<PropertyGroup>
<GenerateDocumentationFile>true</GenerateDocumentationFile>
</PropertyGroup>
By the end, bookapi-minimal.csproj should look like this:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Web">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>net8.0</TargetFramework>
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
<ImplicitUsings>enable</ImplicitUsings>
<GenerateDocumentationFile>true</GenerateDocumentationFile>
<RootNamespace>bookapi_minimal</RootNamespace>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="FluentValidation.DependencyInjectionExtensions" Version="11.9.2" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.OpenApi" Version="8.0.6" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore" Version="8.0.8" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design" Version="8.0.8">
<IncludeAssets>runtime; build; native; contentfiles; analyzers; buildtransitive</IncludeAssets>
<PrivateAssets>all</PrivateAssets>
</PackageReference>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer" Version="8.0.8" />
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools" Version="8.0.8">
<IncludeAssets>runtime; build; native; contentfiles; analyzers; buildtransitive</IncludeAssets>
<PrivateAssets>all</PrivateAssets>
</PackageReference>
<PackageReference Include="Swashbuckle.AspNetCore" Version="6.4.0" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
Now that we have registered the book endpoints in the Program.cs file, we can run the application and test the API endpoints using Swagger.
When you run the application, you should see the Swagger documentation at the following URL: https://localhost:5001/swagger/index.html. The Swagger documentation provides information about the API endpoints, request and response models, and allows you to test the endpoints directly from the browser. You should see something like this:
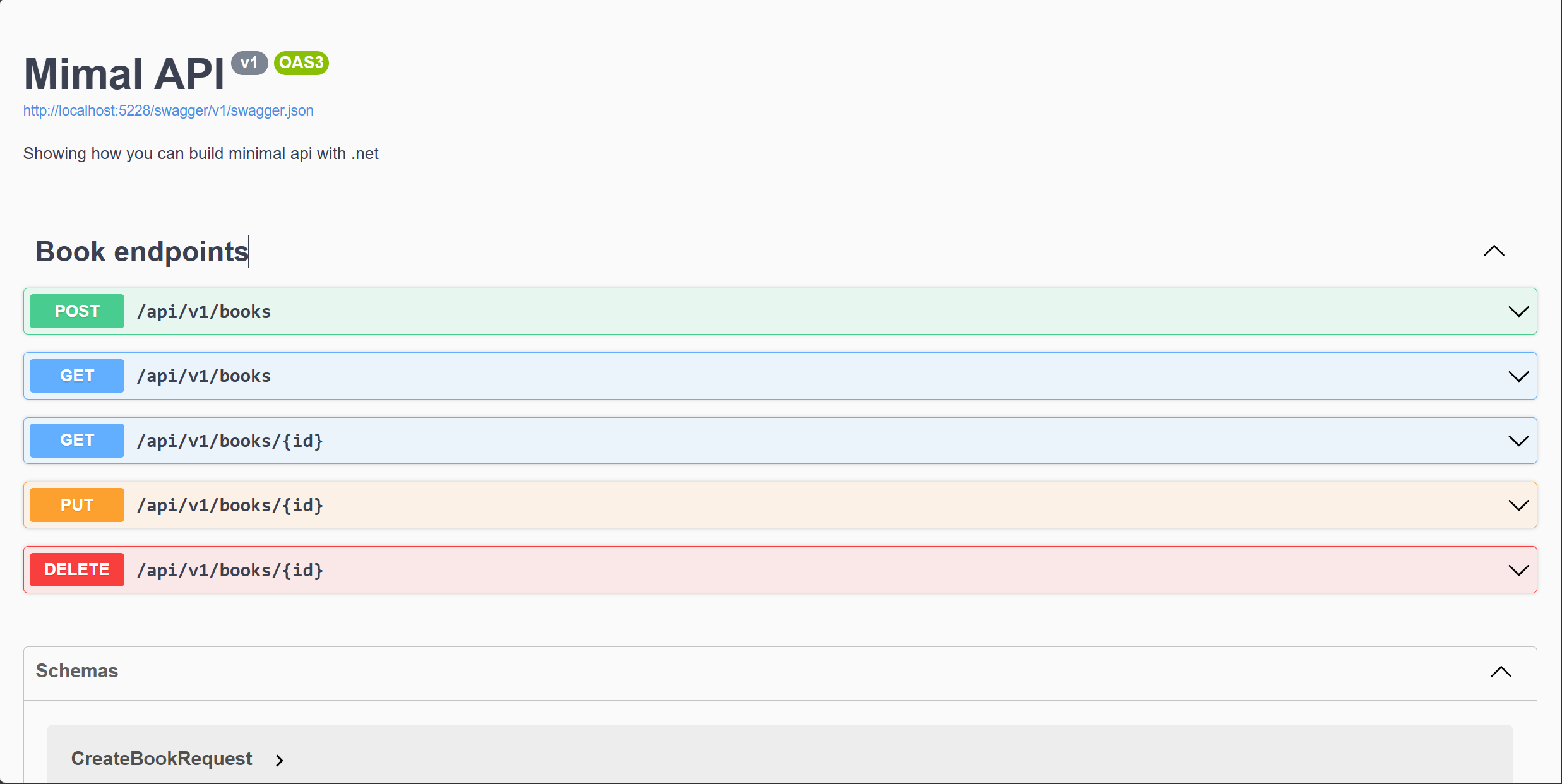
Congratulations! You have implemented the business logic for the book service, created custom exceptions, defined API endpoints, and registered the endpoints in the Program.cs file. You have also enabled Swagger documentation to test the API endpoints.
How to Add Seed Data to the Database
One more important step is to seed the database with initial data when the application starts. This seed data will populate the database, allowing you to test your API endpoints without manually adding data.
Let’s add some seed data before performing migrations and testing our API endpoints.
To achieve this, we will create a new class in our Configuration folder called BookTypeConfigurations and add the following code:
using bookapi_minimal.Models;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Metadata.Builders;
namespace bookapi_minimal.Configurations
{
public class BookTypeConfigurations : IEntityTypeConfiguration<BookModel>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<BookModel> builder)
{
builder.ToTable("Books");
builder.HasKey(x => x.Id);
builder.Property(x => x.Id).ValueGeneratedOnAdd();
builder.Property(x => x.Title).IsRequired().HasMaxLength(100);
builder.Property(x => x.Author).IsRequired().HasMaxLength(100);
builder.Property(x => x.Description).IsRequired().HasMaxLength(500);
builder.Property(x => x.Category).IsRequired().HasMaxLength(100);
builder.Property(x => x.Language).IsRequired().HasMaxLength(50);
builder.Property(x => x.TotalPages).IsRequired();
builder.HasData(
new BookModel
{
Id = Guid.NewGuid(),
Title = "The Alchemist",
Author = "Paulo Coelho",
Description = "The Alchemist follows the journey of an Andalusian shepherd",
Category = "Fiction",
Language = "English",
TotalPages = 208
},
new BookModel
{
Id = Guid.NewGuid(),
Title = "To Kill a Mockingbird",
Author = "Harper Lee",
Description = "A novel about the serious issues of rape and racial inequality.",
Category = "Fiction",
Language = "English",
TotalPages = 281
},
new BookModel
{
Id = Guid.NewGuid(),
Title = "1984",
Author = "George Orwell",
Description = "A dystopian social science fiction novel and cautionary tale about the dangers of totalitarianism. ",
Category = "Fiction",
Language = "English",
TotalPages = 328
}
);
}
}
}
Let’s break down the code above:
In Entity Framework Core, you can use the IEntityTypeConfiguration interface to configure the entity type and seed data for the database. The BookTypeConfigurations class implements the IEntityTypeConfiguration<BookModel> interface and provides the configuration for the BookModel entity.
-
Configure Method: This method is used to configure the
BookModelentity type. It defines the table name, primary key, and properties for theBookModelentity.-
Table Name: The
ToTablemethod specifies the name of the table to be created in the database. In this case, the table name is set to “Books”. -
Primary Key: The
HasKeymethod specifies the primary key for theBookModelentity. The primary key is set to theIdproperty. -
Properties: The
Propertymethod configures the properties of theBookModelentity. It specifies the data type, length, and constraints for each property.
-
-
Seed Data: The
HasDatamethod seeds the database with initial data. It creates threeBookModelobjects with sample data for testing the API endpoints.
Now that we have created the BookTypeConfigurations class, we need to register this configuration in the ApplicationContext class. This ensures that the configuration is applied when the database is created or migrated.
We’re finally almost ready to test our API. But before we do that, we need to perform migrations to create the database and apply the seed data.
Remember that we added our database connection string in the appsettings.json file? Now let’s perform a migration and later update our database for the migration to take effect.
How to Perform a Migration
Migrations allow you to update the database schema based on changes made to your model classes. In Entity Framework Core, you can use the dotnet ef migrations add command to create a new migration reflecting these changes.
To perform a migration, run the following command in the terminal:
dotnet ef migrations add InitialCreate
If the command is successful, you should see an output similar to this:
Build started...
Build succeeded.
Done. To undo this action, use 'ef migrations remove'
You will now see a new folder called Migrations in your project. This folder contains the migration files that were created based on the changes made to your model classes. These migration files include the SQL commands required to update the database schema.
How to Update the Database
After creating the migration, you need to apply the migration to update the database schema. You can use the dotnet ef database update command to apply the migration and update the database. Make sure the SQL Server is running.
Run the following command in the terminal:
dotnet ef database update
This will update the database schema based on the changes made to your model classes. Make sure there are no errors on your database connection string.
How to Test the API Endpoints
Now we can test our endpoints using Swagger. To do this, run the application by executing the following command in the terminal:
dotnet run
This will run our application. You can open your browser and navigate to https://localhost:5001/swagger/index.html to access the Swagger documentation. You should see a list of API endpoints, request and response models, and the ability to test the endpoints directly from the browser.
If your port number is different from 5001, don’t worry – it will still work. The port might change depending on the type of machine you’re using, but it will still achieve the same result.
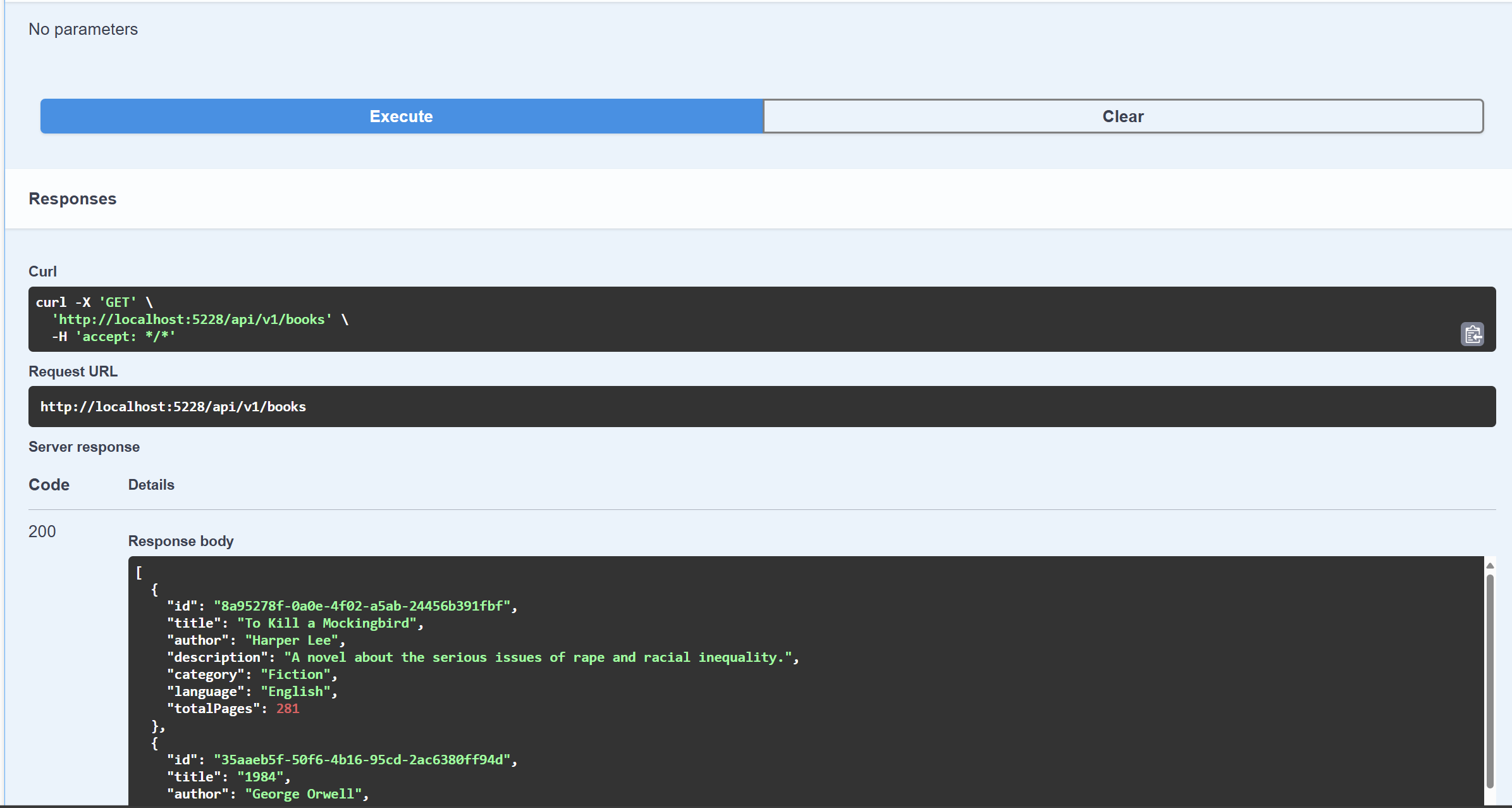
How to Test the Get All Books Endpoint
To test the Get All Books endpoint, follow these steps:
-
In the Swagger documentation, click on the
GET /api/v1/booksendpoint. -
Click the
Try it outbutton. -
Click the
Executebutton.
This will send a request to the API to retrieve all the books in the database.
You should see the response from the API, which will include the list of books that were seeded in the database.
The image below shows the response from the API:
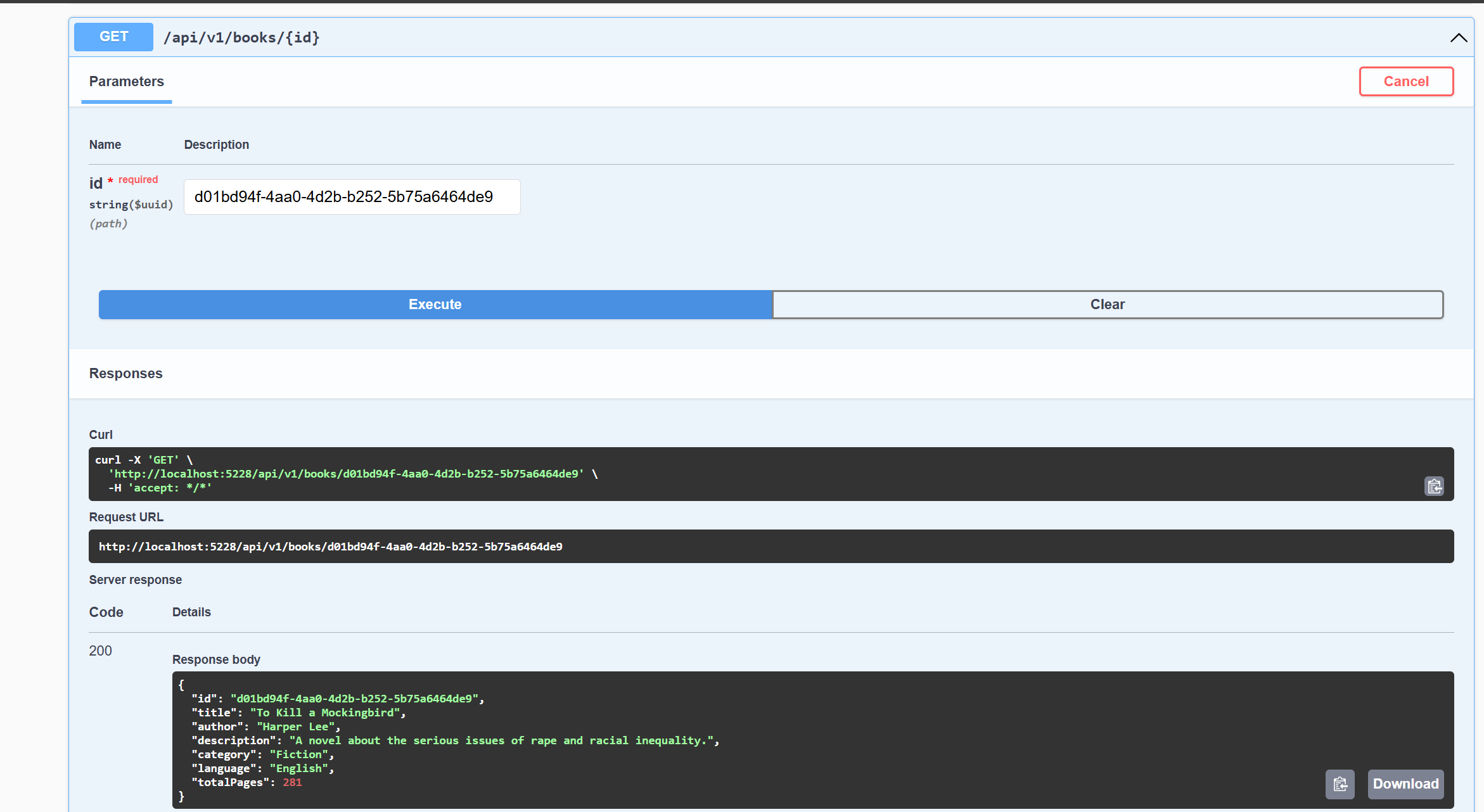
How to Test the Get Book by ID Endpoint
To test the Get Book by ID endpoint, follow these steps:
-
In the Swagger documentation, click on the
GET /api/v1/books/{id}endpoint. -
Enter the ID of a book in the
idfield. You can use one of the book IDs that was seeded in the database. -
Click the
Try it outbutton.
This will send a request to the API to retrieve the book with the specified ID. You should see the response from the API, which will include the book with the specified ID.
The image below shows the response from the API:
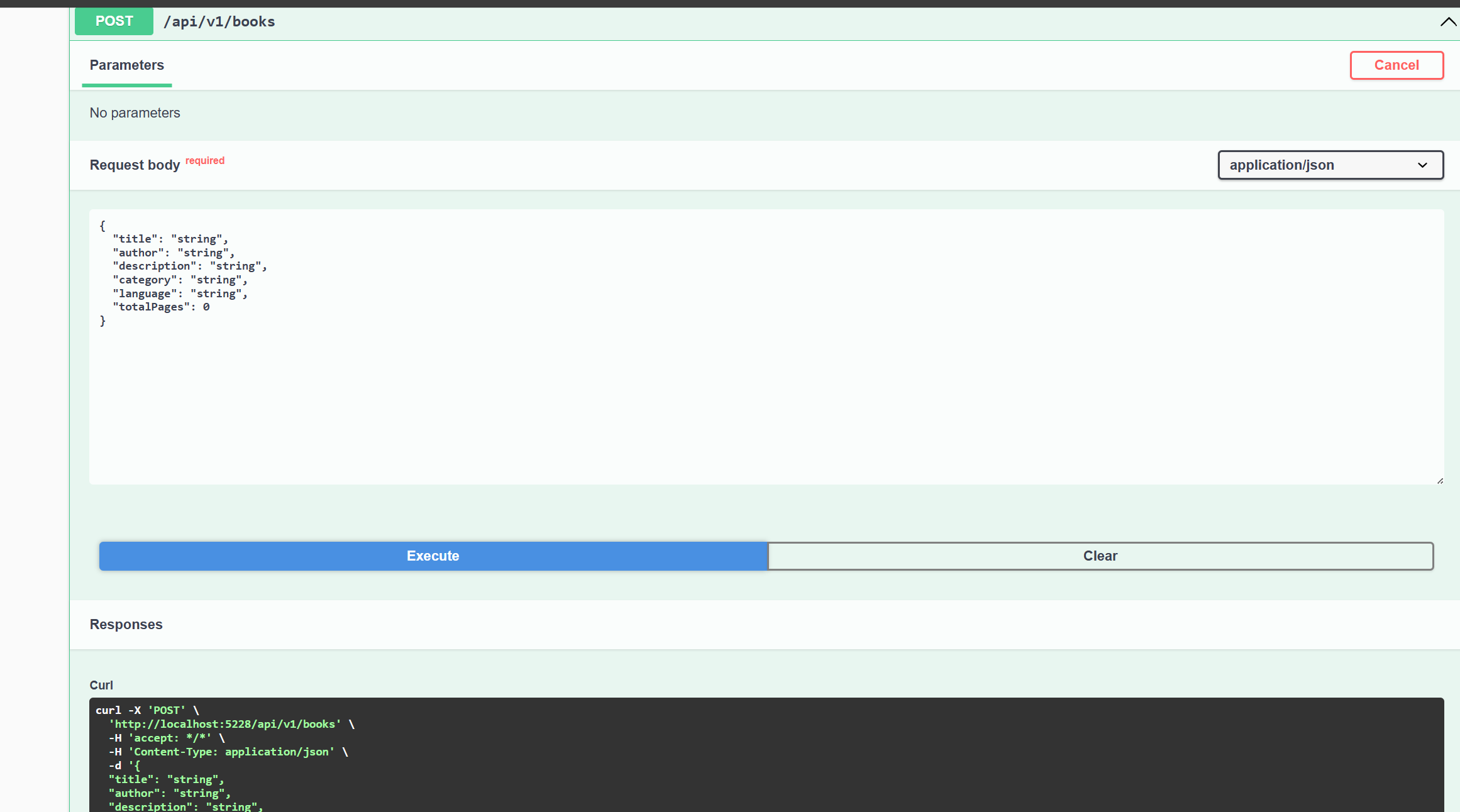
How to Test the Add Book Endpoint
To test the Add Book endpoint, follow these steps:
-
In the Swagger documentation, click on the
POST /api/v1/booksendpoint. -
Click the
Try it outbutton. -
Enter the book details in the request body.
-
Click the
Executebutton.
This will send a request to the API to add a new book to the database.
You should see the response from the API, which will include the newly created book.
The image below shows the response from the API:
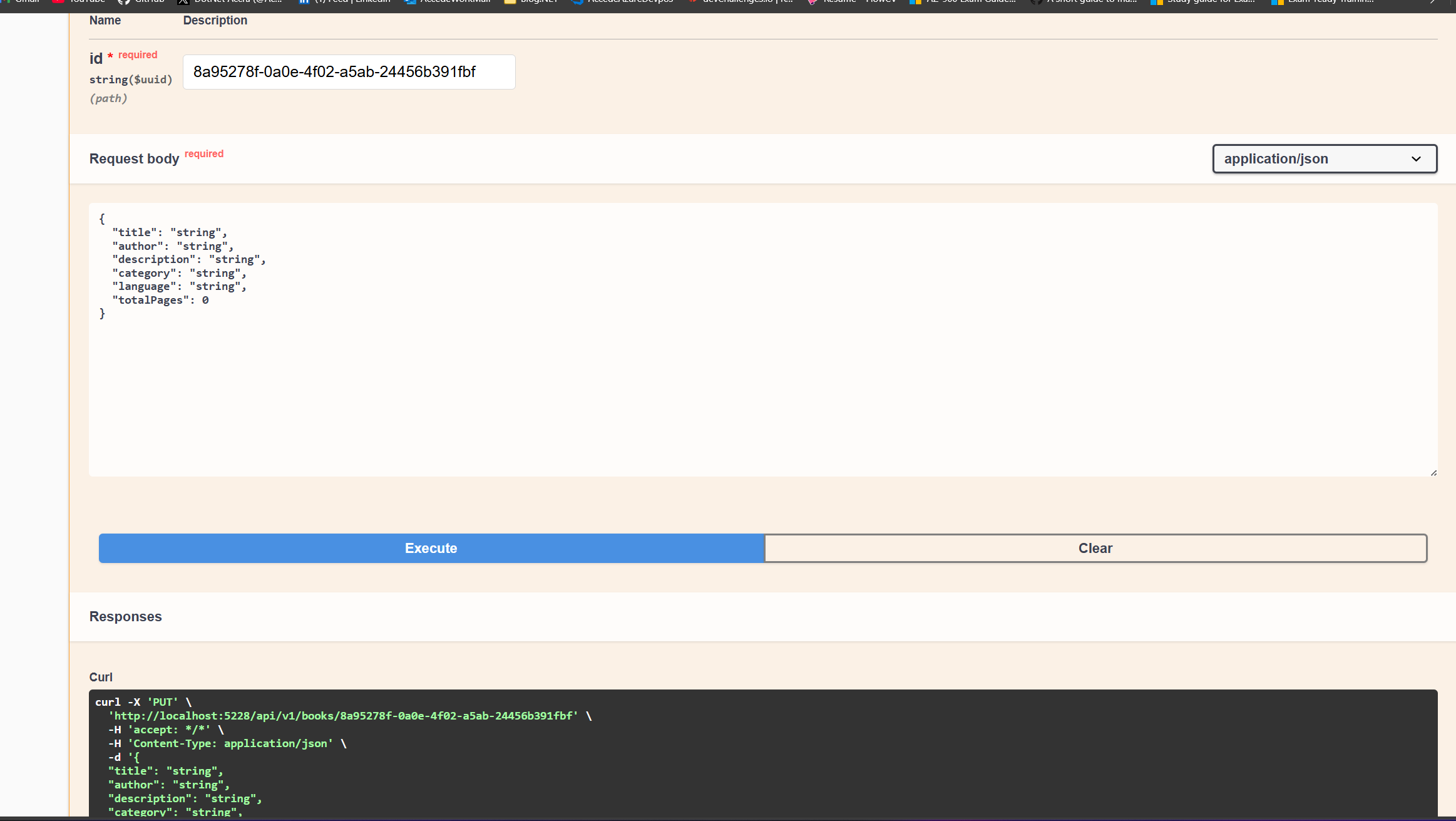
How to Test the Update Book Endpoint
To test the Update Book endpoint, follow these steps:
-
In the Swagger documentation, click on the
PUT /api/v1/books/{id}endpoint. -
Enter the ID of a book in the
idfield. You can use the id of one of the books that we just added. -
Click the
Try it outbutton.
This will send a request to the API to update the book with the specified ID.
You should see the response from the API, which will include the updated book.
The image below shows the response from the API:
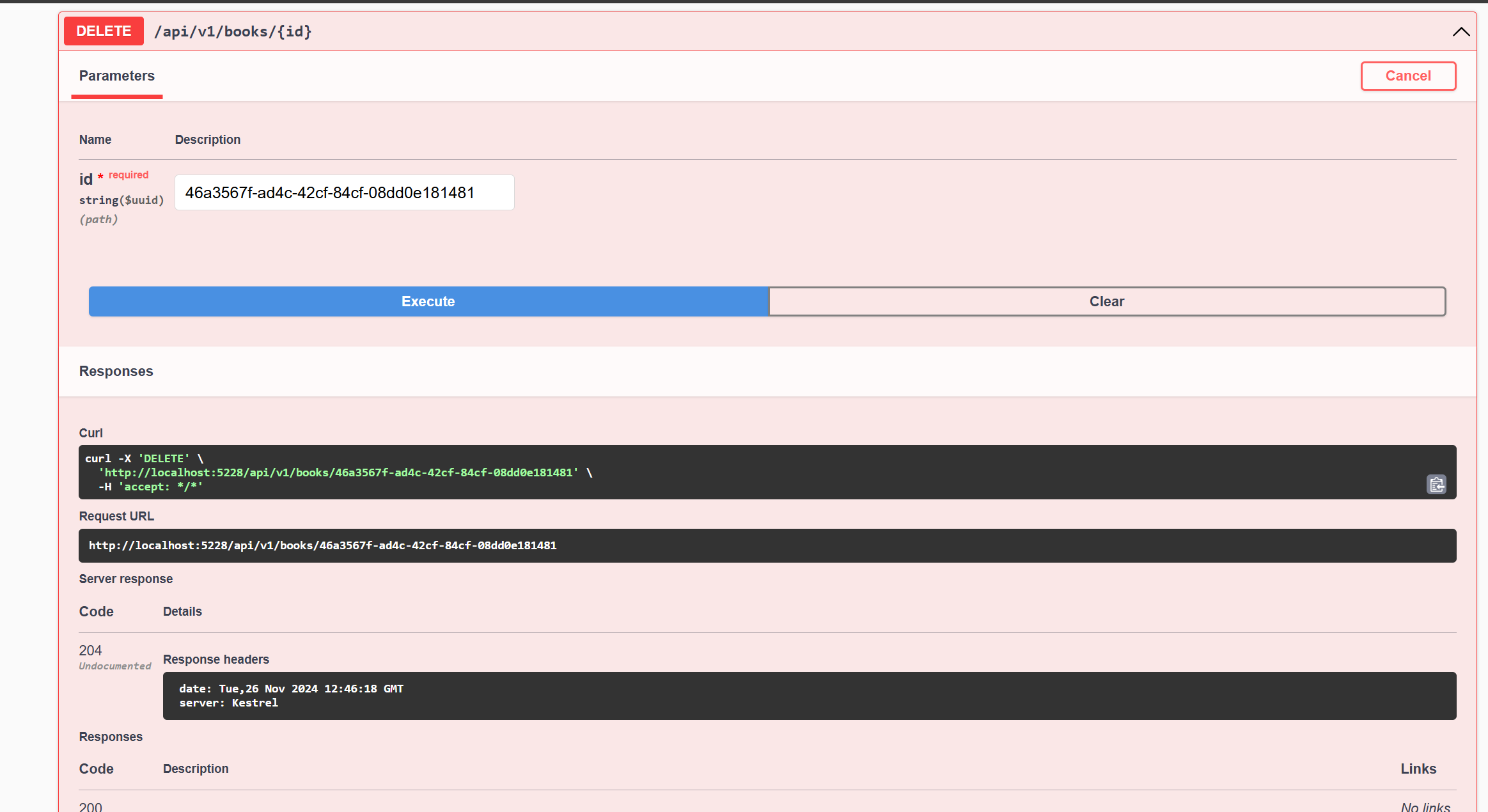
How to Test the Delete Book Endpoint
To test the Delete Book endpoint, follow these steps:
-
In the Swagger documentation, click on the
DELETE /api/v1/books/{id}endpoint. -
Enter the ID of a book in the
idfield. You can use any of the ids from the books that we just added or the seeded data. -
Click the
Try it outbutton.
This will send a request to the API to delete the book with the specified ID.
The image below shows the response from the API:
Congratulations! You have implemented all the CRUD operations for books and tested the API endpoints using Swagger, verifying that they work as expected. You can now build on this foundation to add more features and functionality to your API.
Conclusion
This handbook explored how to create a minimal API in ASP.NET Core with .NET 8. We built a comprehensive book API that supports CRUD operations, implemented custom exceptions, defined and registered API endpoints, and enabled Swagger documentation for easy testing.
Following this tutorial, you have gained a solid foundation for building minimal APIs with ASP.NET Core. You can now apply this knowledge and create robust APIs for various domains and industries.
I hope you found this tutorial both helpful and informative. Thank you for reading!
Feel free to connect with me on social media:

